What Is VMware to AWS Migration?
VMware to AWS Migration is essentially the process of moving on-premises VMware virtual machines (VMs) to the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud. This allows businesses to use AWS cloud capabilities while retaining the familiar functionality of their VMware environment.
In the process of VMware to AWS Migration, businesses can relocate their VMware virtual machines (VMs) from an on-premises VMware vSphere environment to the AWS Cloud. The migration does not require any conversion or re-platforming of the VMs, ensuring a smooth transition and minimal disruption to operations.
Table of Contents
ToggleVMware to AWS Migration Approaches
There are several approaches to VMware to AWS migration, as illustrated in the diagram below:
-
- VM Import: Importing VMware virtual machines (VMs) from an on-premise vSphere environment directly into Amazon.
-
- VMware HCX: Moving VMware VMs from an on-premise vSphere environment to a vSphere environment on AWS, powered by VMware Cloud on AWS.
-
- VMware HCX OS Assisted Migration: Moving VMware workloads not running in vSphere, such as VMware KVM or Hyper-V, to a vSphere environment on AWS, powered by VMware Cloud on AWS.
We will cover each of these approaches in more detail below.
Source: AWS
This is part of a series of articles about Application Migration
Why Are Companies Considering Migrating From VMware? The recent acquisition of VMware by Broadcom, a global technology giant, has led to significant changes in VMware’s licensing model that are prompting companies to reconsider their virtualization strategies. Historically, VMware offered the option to purchase perpetual licenses for its hypervisor product, vSphere, allowing customers to use a specific version of the product indefinitely. Additionally, VMware provided the flexibility to purchase support subscriptions separately, enhancing the value of these perpetual licenses with ongoing support and updates.
However, Broadcom’s strategic shift away from perpetual software licensing towards a subscription-only model has introduced a new financial dynamic for VMware customers. This change not only eliminates the option to buy perpetual licenses but also integrates support directly into the subscription, removing the ability to purchase support separately. This means that customers who previously relied on the cost-effective model of perpetual licenses are now required to commit to recurring subscription payments to continue using vSphere.
Furthermore, Broadcom’s decision to discontinue the free version of vSphere, transitioning it to a paid subscription service, and the sale of VMware Horizon to KKR, has added to the complexity and potential cost for VMware customers. VMware Horizon, a direct competitor to Azure Virtual Desktop, now under different ownership, may lead to uncertainties regarding product direction and support.
These substantial changes have significant financial implications for companies that depend heavily on VMware’s ecosystem. The transition to a subscription model, the integration of support into this model, and the discontinuation of free and perpetual licensing options represent increased and unexpected costs for many businesses. As a result, many organizations are considering moving their VMware infrastructure to AWS or other cloud providers.
Related content: Read our guide to VMware Migration
Benefits of Migrating from VMware to AWS
In addition to the challenges created by VMware’s acquisition, here are some of the key benefits of migration from an on-premise VMware environment to AWS:
-
- Cost savings and operational efficiency: By migrating to AWS, businesses can avoid the high capital expenditure associated with maintaining physical servers and data centers. AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which means you only pay for the resources you actually use. Amazon also provides cloud services that can automate routine tasks and optimize resource usage.
-
- Scalability and flexibility: With AWS, businesses can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand. This capability is particularly useful for businesses with fluctuating workloads, as it allows them to avoid over-provisioning or under-provisioning of resources.
-
- Modernizing applications and infrastructure: By moving to AWS, businesses can leverage the latest cloud technologies to modernize their applications, improve their performance, and enhance their user experience. These include container services, serverless computing, managed databases, cloud-based storage services, and machine learning services.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you successfully migrate from VMware to AWS:
-
Select the best approach based on workload needs
Choose from rehosting, replatforming, or refactoring based on the specific requirements and complexity of your workloads.
-
Optimize network connectivity
Use AWS Direct Connect or VPN for secure and efficient data transfer, minimizing downtime and latency during the migration process.
-
Leverage AWS migration tools
Utilize AWS Migration Hub, AWS Server Migration Service (SMS), and AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) to streamline migration processes, manage dependencies, and ensure a smooth transition.
-
Perform phased migrations with validation checks
Begin with non-critical applications to validate your migration strategy, uncover potential issues early, and refine processes before handling critical workloads.
-
Implement robust post-migration monitoring and optimization
Use AWS CloudWatch, AWS Cost Explorer, and AWS CloudTrail to monitor performance, optimize resource allocation, and manage costs effectively after migration is completed.
VMware to AWS Migration: 3 Approaches
Here are three approaches to migrating your VMware workloads from an on-premise environment to the AWS cloud.
1. VM Import: Import On-Premise VM to AWS Native
Source: VMs in an on-premise vSphere environment (VMware)
Destination: Amazon EC2 instances (AWS native)
Amazon’s VM Import tool enables businesses to import their existing VMware VMs to AWS as Amazon EC2 instances. VM Import supports a variety of VM formats, including VMware VMDK files, and preserves the configuration settings of the imported VMs. This ensures a seamless migration with minimal interruption to operations.
VM Import allows businesses to take advantage of the full breadth of AWS services. Once the VMs are imported as EC2 instances, businesses can leverage AWS’s cloud capabilities to optimize their workloads, enhance their security, and improve their operational efficiency.
However, using this method means the organization must stop using a vSphere management environment and transition its operations to an AWS-based model.
Learn more in AWS documentation: Importing VM as an instance
2. VMware HCX: Import VM to VMware Cloud on AWS
Source: VMs in an on-premise vSphere environment (VMware)
Destination: vSphere environment on AWS (VMware Cloud on AWS)
Another tool that facilitates VMware to AWS Migration is VMware HCX. VMware HCX is a migration service that enables businesses to migrate their on-premises VMware VMs to VMware Cloud on AWS. VMware HCX supports large-scale migrations and offers advanced features such as workload balancing, network extension, and zero-downtime migration.
Moreover, VMware HCX allows businesses to retain their existing VMware environment in the AWS Cloud. This means that businesses can continue to operate their vSphere environment, with familiar VMware tools and processes, while also benefiting from the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of AWS.
There are four ways to migrate VMs using VMware HCX:
-
- Bulk Migration: Bulk migration is a method used for migrating large numbers of VMs simultaneously. This approach is suitable for workloads that can withstand brief periods of downtime. During bulk migration, VMs are powered off on the source site, transferred to the target site in VMware Cloud on AWS, and then powered on.
-
- VMware vMotion: VMware vMotion enables live migration of VMs from the on-premises environment to VMware Cloud on AWS with no downtime. This method is ideal for business-critical applications that require continuous availability. vMotion maintains the continuous service of the VM, ensuring that there’s no disruption in operations and that the memory and state of the VM are kept intact during the migration.
-
- Cold Migration: In cold migration, VMs are powered off in the on-premises environment, then moved to VMware Cloud on AWS, and powered back on. This method is simpler than vMotion but involves downtime for the VMs being migrated. Cold migration is suitable for non-critical workloads that can tolerate some downtime or for VMs that aren’t compatible with vMotion.
-
- VMware HCX Replication Assisted vMotion (RAV): RAV combines the features of both HCX vMotion and bulk migration. It starts with replicating the VM to the target site while the original VM is still operational. Once the replication is near completion, a final vMotion is performed to synchronize the final changes, allowing for minimal downtime. RAV is suitable for migrating VMs with large disks or VMs that require minimal downtime but are not critical enough to necessitate continuous replication.
The following table, provided by AWS, provides the key characteristics of each migration method, which can help you select the best method for your needs.
Source: AWS
Learn more in AWS documentation: VMware HCX migration options
3. VMware HCX OS Assisted Migration
Source: VMware workloads not running in vSphere, such as VMware KVM or Hyper-V
Destination: vSphere environment on AWS (VMware Cloud on AWS)
VMware offers the HCX OS Assisted Migration (OSAM) service. VMware HCX OSAM is a specialized migration service that provides an alternative way to migrate workloads from on-premises environments, whether they are based on VMware or not, to the VMware Cloud on AWS.
VMware HCX OSAM leverages the capabilities of the operating system running inside the VM to facilitate the migration process. It supports a wide range of operating systems and provides a high level of compatibility with various application workloads.
VMware HCX OSAM offers a streamlined migration process with minimal disruption to operations. It enables businesses to migrate their VMs in a staged manner, which helps to manage the migration workload and reduce the impact on operations.
Learn more in VMware documentation: Understanding HCX OS Assisted Migration
Best Practices for a Successful VMware to AWS Migration
Map All Your VMWare Instances
Before initiating a migration from VMware to AWS, it is important to have a comprehensive inventory of all VMware instances. This mapping should include details on each VM’s operating system, configuration, dependencies, and criticality. By understanding the specific requirements and interdependencies of each VM, organizations can plan the migration phases accurately and prioritize which VMs to migrate based on business needs and technical complexity.
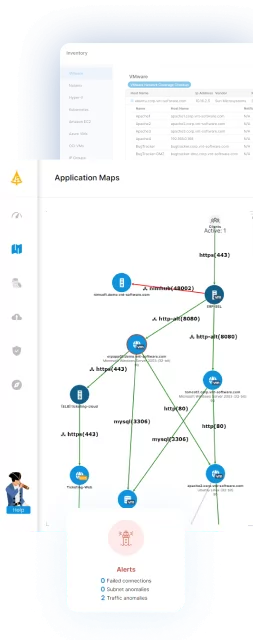
Faddom, a leading application dependency mapping tool, supports both VMware and AWS environments. You can use it to map large-scale VMware environments in minutes and visualize topologies and dependencies. Faddom is fully agentless, meaning you can deploy it in under 60 minutes with no complex configurations.
Learn more about Faddom for data center migration
Establish Fast, Secure Network Connection Between On-Premises Environment and AWS
A robust network connection is crucial for a smooth migration process. AWS Direct Connect provides a dedicated network connection from on-premises to AWS. This ensures high bandwidth, low latency, and secure data transfer.
Implementing VPN connections as a redundancy measure can enhance network reliability. This dual approach guarantees uninterrupted connectivity during migration.
For Large Datasets Consider Using AWS Snowball or AWS DataSync
AWS Snowball and DataSync are services designed to transfer large datasets to AWS efficiently. Snowball is a physical device shipped to transfer data securely, while DataSync automates data transfer over the network.
These services accelerate the migration process for large datasets, reduce data transfer costs, and ensure data integrity. They are ideal for moving terabytes to petabytes of data to AWS.
Utilize AWS IAM to Define Roles and Permissions
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) defines roles and permissions for users and services. It controls access to AWS resources, ensuring security best practices. IAM allows granular control over who can perform actions on resources, limiting potential security risks.
Implementing least privilege access and regularly reviewing permissions enhances security during and after migration. This ensures only necessary access is granted, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Monitor Performance of Workloads on AWS
Monitoring performance is essential for optimizing resource utilization and application performance. AWS provides tools like CloudWatch and CloudTrail for real-time monitoring and logging. These tools offer insights into application health, performance, and operational health.
Setting up alerts for anomalies or performance thresholds ensures proactive management of workloads. This helps in quickly identifying and addressing issues, maintaining high application performance.
Optimize Your Costs
Cost optimization is a key consideration when migrating to AWS. AWS offers various pricing models like On-Demand, Reserved Instances, and Savings Plans. Understanding these options helps in choosing the most cost-effective approach for running workloads.
Implementing cost management tools and practices, such as tagging resources and using AWS Budgets, provides visibility into spending. This enables informed decisions on resource allocation and cost optimization strategies.
VMware Migration Made Easy with Faddom
Faddom’s application dependency mapping provides critical information you’ll need before migrating VMware workloads, automatically discovering all VM instances and their dependencies. Faddom is agentless and doesn’t require credentials to scan your environment. It is cheap, starting at $10K/year, and maps the entire environment in real-time, automatically updating maps 24/7. One person can map an entire data center in an hour.
Learn more about Faddom for data center migration or try it yourself today with a free trial!