What is IT Asset Management?
IT Asset Management (ITAM) is a strategy for overseeing and optimizing the lifecycle of an organization’s IT assets, from procurement to disposal. ITAM involves a systematic approach to managing hardware, software, and information technology infrastructure to ensure that assets are accounted for, deployed, maintained, upgraded, and disposed of efficiently.
This process is critical for maximizing the value of IT assets while minimizing the costs and risks associated with them, including financial waste, licensing penalties, and security vulnerabilities. ITAM provides a framework for organizations to make informed decisions about IT asset procurement, use, and retirement, based on accurate and up-to-date information about the assets’ performance, utilization, and compliance status.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about information security
Table of Contents
Toggle- What is IT Asset Management?
- Why is ITAM Important?
- The IT Asset Management Process
- Tips from the Expert
- 6 Key Benefits of IT Asset Management
- Challenges of IT Asset Management
- Key Features of ITAM Tools
- IT Asset Management Best Practices
- Faddom: Effortless Asset Discovery and Mapping for ITAM
- See Additional Guides on Key Information Security Topics
Why is ITAM Important?
IT asset management helps organizations achieve cost savings by avoiding unnecessary asset purchases and identifying underutilized resources that can be reallocated or retired. Effective ITAM practices also ensure compliance with software licenses and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues and financial penalties. This is particularly important in regulated industries, where software might be subject to strict compliance requirements.
ITAM also enhances operational efficiency and supports strategic decision-making by providing a clear view of the IT asset landscape. This IT visibility allows IT departments to optimize asset utilization, improve service delivery, and align IT investments with business goals.
Learn more in our complete guide to Agentless Scanning or compare between Agentless Scanning vs Agent-based Scanning.
Additionally, ITAM plays a critical role in cybersecurity by ensuring that all assets are properly secured and up-to-date, thereby reducing vulnerabilities and protecting against data breaches and other security threats.
The IT Asset Management Process
The ITAM process includes the following steps:
1. Create an Asset Inventory
The first step is to inventory all IT assets. This involves identifying and cataloging every piece of hardware and software within the organization. An accurate inventory helps organizations understand what assets they own, where they are located, and their status. This knowledge enables companies to make informed decisions about asset procurement, allocation, and retirement.
Learn more in our detailed guide to IT Estate.
Creating a comprehensive asset inventory also lays the groundwork for other ITAM activities, such as lifecycle management and compliance tracking. By maintaining an up-to-date inventory, organizations can ensure that they are fully utilizing their IT assets, avoiding unnecessary purchases, and adhering to licensing agreements and regulatory requirements.
2. Calculate Lifecycle Costs
The next step is assessing the total cost of owning and operating each asset throughout its life, from acquisition to disposal. Understanding lifecycle costs helps organizations identify the value of their IT investments and make cost-effective decisions about procurement, maintenance, and replacement.
Lifecycle cost analysis can also reveal opportunities for cost savings, such as extending the useful life of assets through effective maintenance or identifying more cost-efficient alternatives. By evaluating these costs, organizations can optimize their IT budget and allocate resources more strategically.
3. Tracking
Tracking IT assets involves monitoring the status, location, and condition of all assets in real time. Effective tracking ensures that assets are properly used and maintained, reducing the risk of loss or theft. It also enables organizations to respond quickly to changes in their IT landscape, such as deploying new assets or reallocating existing ones to meet changing business needs.
Tracking is crucial for security, because it provides visibility over assets that need security updates or have entered end of life (EOL). Tracking also facilitates compliance with software licenses and regulatory requirements by providing up-to-date information on asset usage and deployment.
4. Maintenance
Regular maintenance of IT assets is crucial for ensuring their optimal performance and extending their lifespan. This includes scheduling and performing routine checks, updates, and repairs for hardware and software. It reduces the risk of downtime and system failures, and can identify and remediate security vulnerabilities, all of which can have significant operational and financial implications.
A well-structured maintenance program can improve the overall reliability and security of IT assets. By keeping software up-to-date and hardware in good condition, organizations can protect against vulnerabilities and ensure that their IT environment supports business continuity.
5. Cost Optimization
Financial planning enables organizations to budget effectively for IT expenses and optimize their cost structure. This involves forecasting future asset needs, estimating costs associated with acquisition, maintenance, and disposal, and allocating resources accordingly. Cost optimization helps organizations avoid overspending on IT assets and ensures that investments are aligned with business objectives.
Additionally, cost optimization provides insights into the total cost of ownership (TCO) and return on investment (ROI) for IT assets. This information supports strategic decision-making and helps justify IT expenditures to stakeholders. It is especially important in cloud environments, where there is significant potential for cost savings, on the one hand, and cost overruns on the other.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better implement and optimize IT Asset Management (ITAM):
-
Implement automated discovery and updates
Use automated tools for real-time discovery and inventory updates of IT assets to minimize human error and ensure the asset database is always current.
-
Establish strict access controls
Implement role-based access to ITAM systems to prevent unauthorized changes to asset data, protecting against accidental misconfiguration and data breaches.
-
Leverage AI for predictive maintenance
Utilize AI and machine learning to predict asset failures or performance issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing unexpected downtime.
-
Integrate ITAM with procurement systems
Align ITAM with procurement processes to ensure all new acquisitions are automatically registered in the asset management system, improving tracking and compliance.
-
Conduct regular audits and reconciliations
Perform periodic audits to reconcile physical and digital asset inventories, ensuring all assets are accurately accounted for and addressing discrepancies promptly.
6 Key Benefits of IT Asset Management
Here are some of the main advantages of implementing an ITAM strategy:
- Cost reduction: ITAM helps organizations identify unused or underutilized assets, avoiding unnecessary purchases and maximizing the use of existing resources. By managing assets efficiently, companies can significantly reduce costs associated with over-purchasing and maintaining IT assets.
- Enhanced compliance: Through detailed tracking and management of software licenses and hardware assets, ITAM ensures organizations adhere to licensing agreements and regulatory requirements, minimizing legal risks and potential fines.
- Improved security: By maintaining a comprehensive inventory of IT assets and ensuring they are updated and patched, ITAM reduces vulnerabilities and enhances the organization’s security posture, protecting against data breaches and cyber threats.
- Operational efficiency: ITAM provides visibility into the IT asset lifecycle, enabling better decision-making regarding asset procurement, deployment, and retirement. This visibility helps align IT resources with business objectives, improving service delivery and operational efficiency.
- Strategic planning support: Accurate and up-to-date information about IT assets allows organizations to plan for future needs more effectively. ITAM data supports strategic decisions, such as technology investments and IT infrastructure changes, facilitating growth and innovation.
- Sustainability: By managing the lifecycle of IT assets responsibly, including eco-friendly disposal and recycling, organizations can enhance their commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility, aligning with environmental regulations and public expectations.
Challenges of IT Asset Management
While ITAM is critical for organizations with large, dynamic IT environments, there are several challenges to implementing it:
Bridging Multi-Generation Infrastructure
Organizations often operate a mix of old and new technologies, making it difficult to manage and integrate diverse IT assets. This complexity can lead to inefficiencies, compatibility issues, and increased maintenance costs.
Bridging these gaps requires a deep understanding of the lifecycle and capabilities of each asset. By carefully planning upgrades and replacements, organizations can transition smoothly between generations, maintaining operational continuity and leveraging the benefits of new technologies.
Extending Technology Lifespans
As organizations seek to maximize their IT investments, finding ways to prolong the useful life of assets becomes critical. This involves regular maintenance, updates, and strategic refurbishments. However, balancing the need to extend asset lifespans with the desire to adopt new and more efficient technologies requires careful planning and decision-making.
Effective ITAM practices help organizations assess the cost-benefit of extending an asset’s life versus replacing it. By considering factors such as performance, support, and compatibility, organizations can make informed decisions that optimize both operational efficiency and financial outcomes.
Responsible and Sustainable Disposal
As environmental regulations tighten and societal expectations shift towards sustainability, disposing of outdated or unused technology in an eco-friendly manner is increasingly important, both for organizations and society at large. IT asset management must incorporate strategies for recycling, repurposing, or safely decommissioning IT assets, ensuring that disposal practices minimize environmental impact, ensure deletion of sensitive data, and comply with relevant laws.
This challenge also presents an opportunity for organizations to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility. By adopting green ITAM practices, companies can enhance their reputation, contribute to environmental conservation, and potentially realize cost savings through recycling and waste reduction initiatives.
Key Features of ITAM Tools
In a large organization, ITAM is typically practiced via IT Asset Management tools. An ITAM solution typically includes the following features:
Automated Asset Detection
Automated detection enables organizations to identify and catalog IT assets without manual intervention. It scans the IT environment, detecting hardware and software assets across networks. Automated detection ensures that asset inventories are comprehensive and up-to-date, capturing new assets as they are deployed and identifying changes to existing ones.
This feature saves time and reduces the likelihood of errors, and it also provides a foundation for effective asset management. With accurate, real-time data, organizations can make informed decisions about asset allocation, maintenance, and compliance.
License Management
This feature helps organizations track and manage software licenses. It includes monitoring usage, ensuring compliance with licensing agreements, and optimizing license allocations. Effective license management prevents over-provisioning and underutilization, reducing costs and avoiding legal penalties for non-compliance.
License management features can automate renewal notifications and compliance checks, simplifying the complexities of software licensing. This automation supports financial planning and risk management, contributing to the overall efficiency of IT operations.
Version and Patch Management
Version and patch management features enable organizations to track software versions and apply patches and updates systematically. By ensuring that assets are up-to-date, organizations can protect against vulnerabilities, improve functionality, and extend the lifespan of their technology investments.
Effectively managing software versions and patches is also important for compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements, which often mandate specific security practices. Automated tools simplify this process, reducing the workload on IT staff and minimizing the risk of oversight.
Inventory Management
Inventory management provides organizations with visibility into their IT assets. This includes tracking the location, status, and condition of hardware and software. Effective inventory management helps organizations optimize asset utilization, plan for future needs, and ensure compliance with policies and regulations.
Inventory management features often include capabilities for categorizing and grouping assets, facilitating analysis and reporting. This information is useful for strategic planning, budgeting, and IT Audit preparation.
Related content: Read our guide IT Audit Tools and IT Audit Standards.
Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository for information about IT assets and their relationships. It supports asset management by providing detailed insights into how assets are configured and how they interact within the IT environment. This visibility is crucial for change management, incident resolution, and compliance monitoring.
By maintaining an accurate and up-to-date CMDB, organizations can reduce risks associated with changes, improve service delivery, and optimize their IT landscape. The CMDB also facilitates better communication and collaboration among IT teams, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
IT Asset Management Best Practices
Here are some of the best practices for implementing ITAM:
Integrate ITAM with Other ITSM Practices
Integration between ITAM and ITSM ensures that asset management is aligned with broader IT objectives and processes, such as incident management, change management, and service delivery. This integration can improve service quality, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
Collaboration between ITAM and ITSM teams also facilitates a holistic approach to managing IT resources, supporting a more agile and responsive IT environment. This alignment helps meet the evolving needs of the business and deliver value to stakeholders.
Integrate Security and Risk Management Practices into ITAM
Security practices are essential for protecting IT assets and the organization’s data. This involves assessing the security posture of assets, implementing controls to mitigate risks, and regularly reviewing asset vulnerabilities. By embedding security considerations into ITAM processes, organizations can ensure that their IT environment is resilient against threats and compliant with security standards.
This integration also supports a proactive approach to security, enabling IT teams to respond swiftly to emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By prioritizing security within ITAM, organizations can safeguard their assets and data, maintaining trust and operational integrity.
Implement Lifecycle Management
ITAM involves managing each asset from procurement to disposal, ensuring that it delivers maximum value throughout its life. Lifecycle management includes planning for procurement, monitoring performance and utilization, performing regular maintenance, and responsibly disposing of assets.
By adopting a lifecycle approach, organizations can optimize asset use, extend lifespan, and reduce costs. This practice also supports sustainability goals by encouraging the responsible use of resources and minimizing waste.
Monitor and Report on ITAM Metrics
ITAM metrics are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of asset management practices. Key metrics might include asset utilization rates, compliance levels, lifecycle costs, and ROI. By tracking these metrics, organizations can gauge the health of their IT environment, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of ITAM initiatives.
Regular reporting also supports transparency and accountability, helping IT teams communicate successes and justify investments to stakeholders. These insights drive continuous improvement in ITAM practices.
Identify Redundant Assets
Analyzing usage patterns helps organizations identify underutilized or redundant assets. By monitoring how assets are used, IT teams can make data-driven decisions about reallocating or retiring them. This approach maximizes the efficiency of the IT environment and reduces costs by eliminating unnecessary assets.
Regularly reviewing usage patterns also aids in capacity planning and future procurement strategies. It ensures that IT resources are aligned with business needs and that investments are directed towards assets that provide the greatest value.
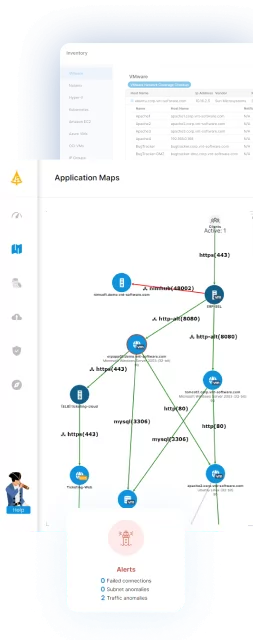
Comprehensively Map Applications and their Dependencies
Comprehensively mapping applications and their dependencies is a critical aspect of effective IT asset management. This process involves identifying all software applications within an organization and understanding how they interact with each other and with the underlying hardware infrastructure.
By creating a detailed map of these relationships, IT teams can gain insights into the complexity of their IT environment, identify potential points of failure, and make informed decisions about asset management and procurement. Mapping applications and dependencies helps organizations manage their IT assets more effectively by ensuring that changes to one application do not inadvertently impact other systems.
Learn more in our detailed guides to:
Faddom: Effortless Asset Discovery and Mapping for ITAM

Faddom helps with IT asset management by visualizing all your on-premises and cloud infrastructure in as little as one hour. Immediately see all your servers and applications and how they are dependent on each other. Start a free trial today!
See Additional Guides on Key Information Security Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of information security.
IT Documentation
Authored by Faddom
- [Guide] IT Documentation: 9 Standards and Best Practices
- [Guide] Network Documentation: What to Document & 4 Best Practices
- [Product] Faddom | Instant Application Dependency Mapping Tool
IT Mapping
Authored by Faddom
- [Guide] IT Mapping: Why You Need It & 4 Ways to Map Your Environment
- [Guide] IT Service Mapping: Capabilities, Process, and Tools
- [Product] Compliance and IT Audit With Faddom
Azure Disaster Recovery
Authored by N2WS