IT infrastructure has become a critical component of today’s business world. As more organizations rely on computing power, storage, and applications, being without these mission-essential assets is an almost unfathomable thought, underpinning the importance of investing in disaster recovery. This glossary explores what disaster recovery is, why it matters, and what goes into developing an effective disaster recovery plan.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about hybrid cloud.
Table of Contents
Toggle- What is Disaster Recovery?
- What is Business Continuity?
- Why should you invest in disaster recovery?
- How does disaster recovery work?
- What is a disaster recovery plan?
- What are the components of an effective disaster recovery plan?
- Tips from the Expert
- What are the types of disaster recovery?
- Streamline your disaster recovery planning
- Learn More About IT Disaster Recovery
- See Our Additional Guides on Key Hybrid Cloud Topics
What is Disaster Recovery?
Disaster recovery is the process organizations follow to reinstate their IT infrastructure after a disruptive event. Disasters take many shapes and forms and can include cyber-attacks, natural disasters, theft or sabotage, power failures, IT network failures, events affecting an organization’s reputation, and also outbreaks of diseases or infections that impact operations. Read more about ransomware disaster recovery and disaster recovery software.
What is Business Continuity?
Business continuity is a systematic approach to reestablishing an organization’s full functionality. While business continuity and disaster recovery sound like one and the same thing, disaster recovery is an aspect of business continuity. Where business continuity plans address an organization’s return to full functionality, disaster recovery plans focus on reestablishing an organization’s IT infrastructure.
Why should you invest in disaster recovery?
Disaster recovery offers organizations a means of salvaging their operational capacity and can save them from devastating losses that could lead to a complete shutdown. By investing in disaster recovery, organizations can build more resilience and a stronger competitive advantage. Here are six reasons to invest in disaster recovery:
- Prevent Revenue Loss: As more businesses rely on technology to operate, IT infrastructure holds tremendous value. Without an operational IT infrastructure, businesses can suffer significant revenue losses.
- Enhance resilience: Committing to disaster recovery can be costly, however, it improves an organization’s ability to quickly return to business as usual after a disaster. Through regular DR testing, organizations developed the resiliency they need to limit the effects of disasters on their operations.
- To Maintain Customer Satisfaction: DR plans tested develop resilience that pays dividends over time. It’s a well-known fact that customer acquisition costs exceed customer retention costs. By being prepared for disasters, customer attrition is limited if not averted altogether.
- Improve partner and supply chain confidence: Due to the connectedness of organizations and their reliance on partner resources and infrastructure, investing in DR can improve relationships and confidence. Short recovery time objectives or RTOs and recovery point objectives or RPOs, as a result of DR planning and investment, are viewed as a commitment to meeting service level agreements, making a stronger case for long-lasting relationships.
- Hardware failure is possible: IT hardware is machinery and, therefore, prone to breakdown and failure. Having a DR plan accounts for outages and prevents unnecessary downtime.
- Compliance: As security and privacy grow in importance, new regulations are introduced to protect sensitive information. Investing in a DR plan ensures that you stay ahead of compliance requirements.
How does disaster recovery work?
Disaster recovery typically leverages off-premise resources like computer processing and storage to regain IT operational functionality. When a disaster occurs, these resources are used to recover data, applications, and servers. Effective disaster recovery is also only possible with a disaster recovery plan.
What is a disaster recovery plan?
A disaster recovery plan is a documented approach for the restoration of business data and applications from a data backup image. It involves various elements and steps that must be followed to regain a functional IT infrastructure.
What are the components of an effective disaster recovery plan?
For a disaster recovery plan to be successful, it must include the following components:
The right personnel
Personnel is integral to seeing through a successful disaster recovery plan. It’s essential to create a team that includes crisis management, business continuity, impact assessment and recovery, and IT applications personnel. When establishing a DR team, include backup staff capable of performing tasks should key team members are unavailable.
Other essential team members include executive management to oversee budgets, approvals, and policies, and at least one representative from each critical business unit who will provide feedback on DR effectiveness.
Complete an IT inventory
Create a record of all hardware and software assets, including all cloud-based infrastructure and applications. Documenting the IT infrastructure daily and possessing a fresh accurate assessment of the topology is key to indicate which assets are owned or rented, which are business-critical, and whether they have any application dependencies
Establish backup procedures
Determine a complete guide on how data is to be backed up, where it will be stored (including folder locations and servers), and how it will be recovered.
Create disaster recovery procedures
Create procedures that explain in detail what emergency responses exist, including how to implement them. Disaster recovery procedures should account for mitigation procedures, limitation of damages, last-minute backups, and remediation of cybersecurity threats.
Designate disaster recovery sites
Identify the type of disaster recovery site (hot, warm, or cold site) you’ll use as an alternate data center.
Implement restoration procedures
Execute all procedures meticulously, ensuring that all steps are performed in sequence and according to procedural specifications.
Test your DR plan regularly
To ensure preparedness, it’s wise to test your procedures often. Simulating DR scenarios will keep teams trained and capable of dealing with DR events, and help decrease downtime when events occur.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you enhance your disaster recovery planning and execution:
-
Prioritize recovery based on business impact
Rank systems and applications by their criticality to operations, and allocate recovery resources accordingly to minimize business disruption.
-
Implement cross-training for DR teams
Ensure team members are trained in multiple roles to avoid single points of failure if key personnel are unavailable during a disaster.
-
Use tiered backup strategies
Combine local, off-site, and cloud backups to balance recovery speed, cost, and resilience for various data and systems.
-
Continuously monitor DR dependencies
Use dependency mapping tools to keep up-to-date on how applications, servers, and networks interact, ensuring no blind spots in your DR strategy.
-
Integrate DR drills into regular operations
Make testing part of routine IT operations to normalize procedures, refine processes, and reduce downtime during real events.
What are the types of disaster recovery?
There are various disaster recovery methods available that can be used individually or together. Disaster recovery methods include:
-
- A hot site is a mirror copy of the primary production center, a hot site is the most expensive solution given the cost to recreate a primary site. Backups to hot sites take place in real-time.
-
- A warm site is a facility with network connectivity and the required hardware is pre-installed, however, it isn’t capable of the same capacity as a primary site. Warm site backups occur daily or weekly. Warm sites are best suited for organizations that can withstand short interruptions and have less critical data to recover.
-
- A cold site is an office space with basic utilities including power, a cooling system, air conditioning, and communication equipment. IT staff to physically relocate hardware to cold sites and make them functional and relieve the load of primary hardware. Due to the work involved in relocating hardware, cold sites require the most time to set up.
-
- Disaster Recovery as a Service or DRaaS solutions provide organizations with cloud-based computing capability, allowing them to continue to operate from the vendor’s cloud. Latency is a key consideration when selecting a DRaaS provider, as it can directly affect your capabilities.
-
- Backup as a Service or BaaS enables software backups to a third-party provider. Unlike a DRaaS, infrastructure is not provided by backup providers, leaving affected organizations with the responsibility of getting hardware back online and then retrieving data from their BaaS provider.
-
- Datacenter disaster recovery solutions protect infrastructure, allowing for quicker recovery times. This is achieved by installing fire suppression systems that prevent damage and downtime and adding uninterrupted power supplies to prevent downtime caused by unexpected or planned power outages.
-
- Virtualization leverages off-site virtual machines that can store backups of specific operational services, including data or a functional replica of an organization’s entire computing environment. Virtualization speeds DR execution as it can be automated.
-
- Point-in-time copies or point-in-time snapshots are backups of an entire database captured at a specific time and stored off-site.
-
- Instant recovery, unlike point-in-time copies, captures a snapshot of an entire virtual machine. These snapshots can be used to run critical applications while the primary VM is being restored.
Streamline your disaster recovery planning
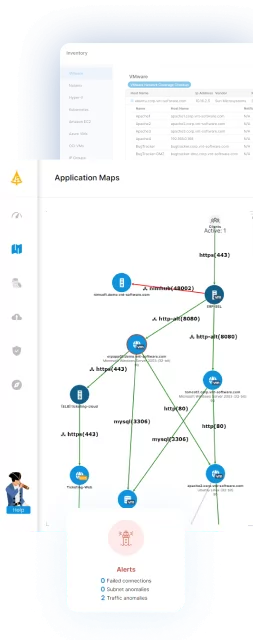
Effective disaster recovery planning involves a complete documentation of the entire IT environment from inventory to understanding all the connections, relationships and dependencies between servers, business applications and subnets. Faddom’s application dependency mapping tool discovers and maps business application dependencies in only 30 minutes. It is a 100% non-intrusive solution. It’s also agentless, credential-less, so there is no need to reconfigure firewall rules – we work completely passive using network traffic protocols only(IP address based) and map automatically 24/7 and in real-time so our maps are always up-to-date.
Learn More About IT Disaster Recovery
How to Develop a Ransomware Disaster Recovery Plan
66% of surveyed organizations experienced a ransomware attack last year. It was 37% in 2020. The cost is $1,467 per minute of downtime.
Read more: How to Develop a Ransomware Disaster Recovery Plan
Disaster Recovery Software for Backing Up Virtual Servers to the Cloud
If you’re backing up your servers and not using a cloud platform, you can’t use disaster recovery software effectively at all.
Read more: Disaster Recovery Software for Backing Up Virtual Servers to the Cloud
How to Create an IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Disaster recovery is a subset of every organization’s business continuity plan, which provides approaches for the entire business.
Read more: How to Create an IT Disaster Recovery Plan
IT Resilience: What is It?
IT resilience focuses on making all IT assets and their services and processes available and protected from disruptions at all times.
Read more: IT Resilience: What is It?
See Our Additional Guides on Key Hybrid Cloud Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of hybrid cloud.
Cloud Migration
Authored by Faddom
- [Guide] Data Center Migration: Complete Guide 2025
- [Guide] Cloud Migration to AWS: 3 Phases, 7 Rs and 5 Free Tools to Get You Started
- [Blog] How Secure is the Cloud?
- [product] Faddom | Instant Application Dependency Mapping Tool
Nutanix
Authored by Faddom
-
[Guide] Nutanix vs. VMware: 5 Key Differences and How to Choose
-
[product] Faddom | Instant Application Dependency Mapping Tool
Data Privacy
Authored by Imperva