Those who still rely on perimeter controls to protect their data centers probably already know that their security solutions are in need of updates.
In this post, we will look at why network segmentation through VLANs or traditional firewalls is insufficient for today’s hybrid and dynamic environments, the trend of adopting micro-segmentation as a popular alternative, the use cases for microsegmentation, microsegmentation for compliance and risk reduction, how to avoid under- and over-segmenting networks, and using visibility as a foundational first step. (For more information, see our Guide to Microsegmentation.)
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Limitations of Traditional Security Controls in Today’s Data Center
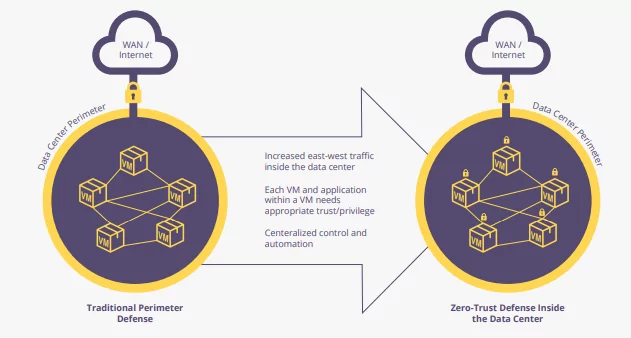
Modern enterprises are totally different beasts from the way that businesses worked even a decade ago. Historically, security focused on perimeter controls that guarded traffic north-south, in and out of the data center. The rise in cloud computing, reliance on third-party vendors and software, and devops-style agile development practices have increased the amount of traffic that moves inside data centers, east-west. Most estimates put internal traffic at around 80% of all communications, meaning that security needs to follow suit.
Some businesses are using traditional security controls to beat this modern-day problem, relying on VLANs and enforcing communication through firewalls and ACLS. At first glance, this may seem like a great idea. After all, VLANs do not need any updates to infrastructure or tools, right? Wrong.
Here are the main problems with using this approach.
Manual configuration: Network and application changes are a lot of work when you need to make every configuration manually.
Resource-heavy: Your engineers will need to configure switches and connect servers, all to prepare the network for the VLANs. Application teams will also need to allocate resources to building code, discovering infrastructure, and preparing any other applications that will be affected by the change. You will also need to submit firewall change requests and involve firewall governance teams.
Time-intensive and slow: This process will take many months, and that’s assuming you have a good map of your environment to begin with. When devops pipelines are being used, this is just not good enough.
Maintenance costs: With two teams and a whole lot of resources and downtime you can expect a hit to your bottom line.
Related content: Read our guide to network address translation
Customer experience: Once you’re ready to start creating security policy for this new VLAN, you’ll have to warn customers of downtime while you reconfigure applications, IP addresses, and integrations.
Perhaps you could look beyond these startup costs to time and resources, if the solution itself would be effective once you got it up and running. Unfortunately, VLANS are a limited technology at best. Which brings us to the most important point.
Limited ability to secure: VLANs do not extend their security to the cloud or to modern systems such as containers. This technology also doesn’t provide any whatsoever, which means you can’t be certain that you are securing the right applications, workloads, or communications. This is also relevant for compliance and governance.
This is part of a series of articles about IT Mapping
The Benefits of Microsegmentation
In contrast, the best microsegmentation was built for modern day environments, including cloud and container technology. It doesn’t involve manual configuration or heavy resource-needs, and it shows quick time to implement and see value from. Here are the top four benefits you can expect to see when adopting microsegmentation as your security technology of choice.
1. Risk Reduction
Hybrid cloud environments, in particular, greatly increase your businesses’ attack surface. Application activity in this kind of heterogeneous environment needs tight controls.
Microsegmentation is known to support businesses in working towards creating a zero-trust model. Zero-trust, coined by Forrester in 2010, is a security method in which users, data, applications, and workloads are given the access they need — and no more. The principle of “assume access” means that you assume an attacker has already made it through your external perimeter. How are you going to ensure that they get no further?
By creating segments inside your network, you can reduce the attack surface substantially. Even if a breach were to occur, the attacker could only move within that specific segment and nowhere else. One good example that is a common starting point for businesses implementing microsegmentation technology is to create segments for your production and development environments — a practice known as environment segmentation.
2. Stopping Lateral Movement
Once a breach has made its way through your perimeter, traditional security controls are not enough to limit their reach. In fact, there is nothing to stop attackers from making what’s known as lateral movement, east-west inside your data center, escalating credentials or permissions to make it to sensitive data or critical assets.
In many cases, organizations would not even know that there is anything amiss. As we discussed, up to 80% of all communications and traffic happens inside the data center, giving attackers plenty of opportunities to blend in with the crowd.
3. Achieving Compliance
Compliance is big business in today’s threat landscape, and any business that deals with customer data needs to be aware of the regulations that pertain to their organization. For financial organizations that would be PCI-DSS, for healthcare, it’s HIPAA. For general customer interaction, EU businesses need to be aware of GDPR. Organizations in the US should brush up on CPA.
No matter which regulations you’re bound by, protecting personal information is number one on the list. This usually involves your company working out what is “in scope” and then keeping it separate, or segmented, from the rest of your data center. Microsegmentation is perfect for this use case — and with the right visibility, you can simply isolate the applications and workloads that carry this sensitive information and ensure that it is protected in case of an attack.
While incidents do happen — and it’s impossible to be prepared for everything — you can rest assured that you have done your part to protect your customers and your business’ reputation and have an audit trail to provide to regulators to prove this compliance.
4. Securing Digital ‘Crown Jewels’
The benefit of microsegmentation as opposed to other controls is its platform-independence and its granularity. This means that specific sensitive assets or “crown jewels’ can be protected with as much enforcement as you would like — keeping your most valuable applications and data secure, even in case of a live breach.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better protect data centers using network microsegmentation:
- Leverage dynamic policies for agility
Use dynamic policies that adapt to changes in your environment automatically, such as the addition of new VMs or containers. This ensures that your microsegmentation strategy remains effective as your infrastructure evolves. - Incorporate machine learning for anomaly detection
Implement machine learning algorithms to detect and respond to anomalous behavior within segments. This helps in identifying potential breaches or misconfigurations that static rules might miss. - Integrate microsegmentation with SIEM solutions
Link your microsegmentation tools with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for enhanced visibility and threat detection across your segmented network. This integration enables quicker incident response and better correlation of security events. - Focus on critical applications first
Begin your microsegmentation efforts by protecting the most critical applications and data. This approach reduces complexity and ensures that your most valuable assets are secured while you refine your broader segmentation strategy. - Regularly review and optimize segmentation policies
Continuously assess and refine your segmentation policies to address any emerging threats or changes in business operations. Regular reviews help maintain an optimal balance between security and operational efficiency.
The Risks of Under- and Over-Segmenting Your Network
Microsegmentation technology needs to be implemented with a smart balance. The tighter the segments, the more secure they will be — but this will have a direct impact on your business’ flexibility and adaptability. If, however, you create a coarser microsegmentation policy to ensure that you have more freedom, the attack surface could well be too large to ensure that you have adequately reduced risk.
It’s a tough problem to solve. Over-segmentation could have an adverse effect on your business processes. (According to Garter, more than 70% of segmentation projects will have their initial design rearchitected because of over-segmentation.) On the other side of the coin, under-segmentation could leave you open to attack.
In this reality, many microsegmentation projects fail, making it more important than ever that you begin with strong visibility into your entire infrastructure so that you will be sure that you have a full grasp of the balance that you need.
Security Starts with Visibility
Microsegmentation is a powerful technology and is worthy of all the hype that’s surrounding its entry into the cybersecurity market. However, before you start seeing the value to compliance, risk reduction, and general security posture, you need to start with an accurate picture of your entire environment from end to end. After all, how can you secure what you cannot see? (Go here to learn about mapping your entire IT systems in as little as 60 minutes!)
Visibility technology is not all created equally, and the wrong choice could leave you with gaps or blind spots. In turn, this could create under- or over-segmentation of your projects or lead to a dangerously wide attack surface that leaves you open to unnecessary risk.
Here are the top features to look out for when choosing a visibility platform:
1. Platform independent
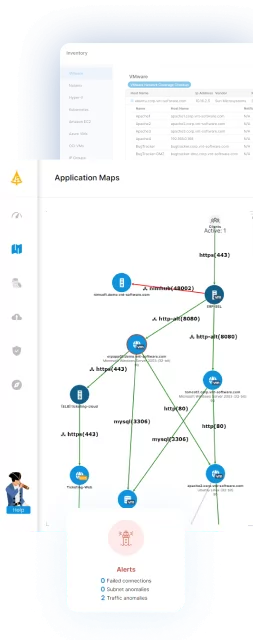
Visibility only works if you can see everything. Some vendors give cloud coverage while others work on-premise. Integrating disparate solutions adds complexity and hassle. Don’t accept less than one map that shows you everything from legacy infrastructure through to container systems and cloud — and works with all operating systems and platforms as well.
2. Agentless
Agents and credentials will slow you down, no matter what your provider says. Wire data as opposed to machine data provides all the accuracy you need, with zero impact on performance and much faster time to implementation and value.
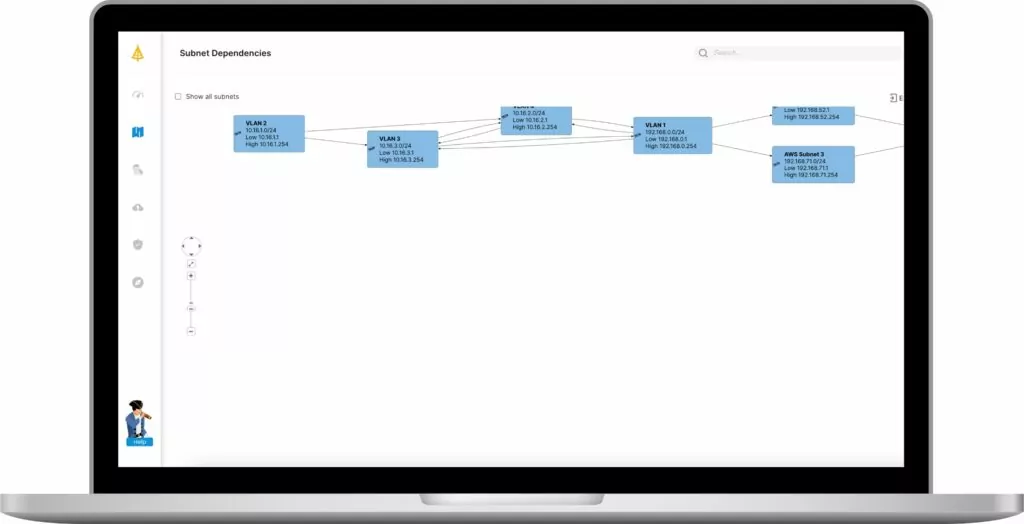
3. Application dependencies
Native cloud solutions will visualize applications and servers but won’t show you the dependencies and communications. When planning a complex project like micro-segmentation, you need to be able to see, at a glance, the impact of any policies. Application dependencies to a granular level are essential because they can alert you to issues such as blocked ports.
4. Accurate and real-time
Continuous scanning is a must-have because it provides a real-time view of your data center instead of remaining reliant on scheduled scanning that happens during “off hours.” Continuous scanning gives you an accurate view of what’s happening in your real-life setting, not a snapshot of a specific time of day.
5. Intuitive
Many vendors provide complex lists of data that are difficult for even the tech-savvy to understand. In contrast, look for a partner that provides a clear, easy-to-read map. It should be easy to share with business stakeholders and customizable for the information that you want to filter and see. The easier it is to use, the easier it will be to get buy-in when you’re ready to build policy.
Your cannot microsegment your environment unless you have a full map of your system first. Learn more about Faddom today!