What is Network Mapping?
Network mapping is the process of visually representing a network’s structure, including its devices, connections, and topology. It helps IT teams understand how network components interact, identify vulnerabilities, and troubleshoot issues efficiently.
Network maps can be created manually or with automated tools that scan the network to detect devices, IP addresses, and data flows. These maps can be presented as diagrams showing physical layouts, logical relationships, or both.
Common use cases include security analysis, performance monitoring, and compliance auditing. By maintaining an up-to-date network map, organizations can improve security, optimize performance, and streamline network management.
This is part of a series of articles about IT Mapping
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are Network Mapping Tools and Software?
Network mapping tools show the connectivities of all local physical devices and collect real-time data from them to create relevant reports. For example, the software can monitor performance, identify inefficiencies, show bottlenecks, and uncover hidden items.
In the past, network administrators manually drew visual depictions of their networks on one page. Of course, it would take a lot of time, and the IT staff would have to change the chart whenever a new device was set up or taken down. But today, network mapping software can automatically discover the network topology and all connected devices.
Why is Network Mapping Omportant?
Network maps help with network visualization, device monitoring, and network diagnosis. For example, imagine that a company has installed new software that consumes too much data. Perhaps the application has bugs or is experiencing an error. Finding that specific software, identifying the problem and resolving it can be done much more quickly and easily with network maps.
In general, network maps can also help to address compliance issues, automate additional IT processes, optimize networks, save time, and see live traffic, top protocols, uptime, downtime, network coverage, and data volume in a single dashboard with associated reports.
Key Features of Network Mapping Tools
Network mapping software offers a range of features that help IT teams visualize, monitor, and manage network infrastructure efficiently. These tools provide real-time insights, automate discovery, and enhance security. Below are the essential features of network mapping software:
- Automated discovery: Scans the network to detect devices, connections, and topology in real time, reducing the need for manual input.
- Visual network representation: Provides interactive diagrams that illustrate physical and logical relationships between devices.
- Real-time monitoring: Continuously tracks network status, traffic patterns, and performance metrics to detect anomalies.
- Customizable alerts: Notifies administrators of connectivity issues, high bandwidth usage, or security threats.
- Device and IP address management: Helps track and manage IP allocations, identify unauthorized devices, and prevent conflicts.
- Security analysis: Identifies vulnerabilities, unauthorized access points, and potential threats within the network.
- Performance optimization: Highlights bottlenecks, latency issues, and inefficiencies to improve overall network performance.
- Integration with IT systems: Connects with network monitoring, security, and IT asset management tools for centralized oversight.
- Compliance reporting: Generates reports for audits and regulatory requirements, ensuring adherence to industry standards.
- Scalability: Adapts to growing networks by dynamically updating maps as new devices are added.
8 Notable Network Mapping Tools
1. Faddom
Faddom provides a powerful, agentless network mapping platform that offers a real-time, interactive view of your IT infrastructure. It automatically discovers all network components, connections, and dependencies, enabling IT teams to enhance troubleshooting, security, and compliance without interrupting operations.
Key features include:
- Agentless asset discovery: Instantly maps all network connections and dependencies without impacting performance.
- Real-time traffic analysis: Detects unexpected connections, bottlenecks, and anomalies to improve security and efficiency.
- Hybrid IT visibility: Covers both on-premise and cloud environments.
- Change impact analysis: Helps IT teams anticipate risks before modifying the infrastructure.
- Comprehensive documentation & compliance: Keeps an up-to-date, audit-ready map for governance and IT management.
- Seamless integration: Works alongside ITSM, SIEM, and monitoring tools for a unified view of network dependencies.
2. Nmap
Nmap (Network Mapper) is an open-source network scanning tool for discovering hosts and services within a network. It achieves this by sending packets to target devices and analyzing their responses. Originally developed for Linux, Nmap is now available on multiple platforms, including Windows and macOS.
Key features include:
- Fast scan: Performs quick port scans (nmap -F) to provide rapid results.
- Host discovery: Identifies active devices on a network by analyzing responses to TCP, ICMP, or port requests.
- Port scanning: Detects open ports on target hosts, helping assess security risks.
- Version detection: Determines the software versions running on networked services.
- Ping scan: Checks the availability of hosts by sending ping requests.
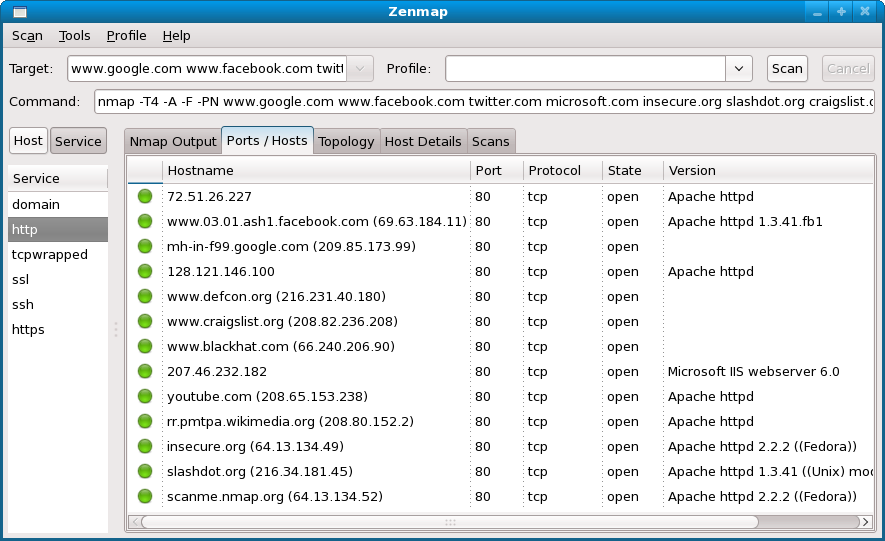 Source: Nmap
Source: Nmap
3. Solarwinds Network Topology Mapper

SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM) is an automated network mapping tool to discover, visualize, and maintain up-to-date network topology maps. It uses various discovery protocols, including ICMP, SNMP, WMI, CDP, and VMware, to identify devices and their connections.
Key features include:
- Automated network discovery: Scans the network to detect devices and connections.
- Network topology: Builds hierarchical diagrams representing logical and physical relationships between devices.
- Network diagrams: Generates network maps that adapt to changes in the infrastructure.
- Topology change detection: Monitors the network for modifications and updates maps accordingly.
- Network compliance support: Helps meet compliance requirements (e.g., PCI) by maintaining network diagrams.
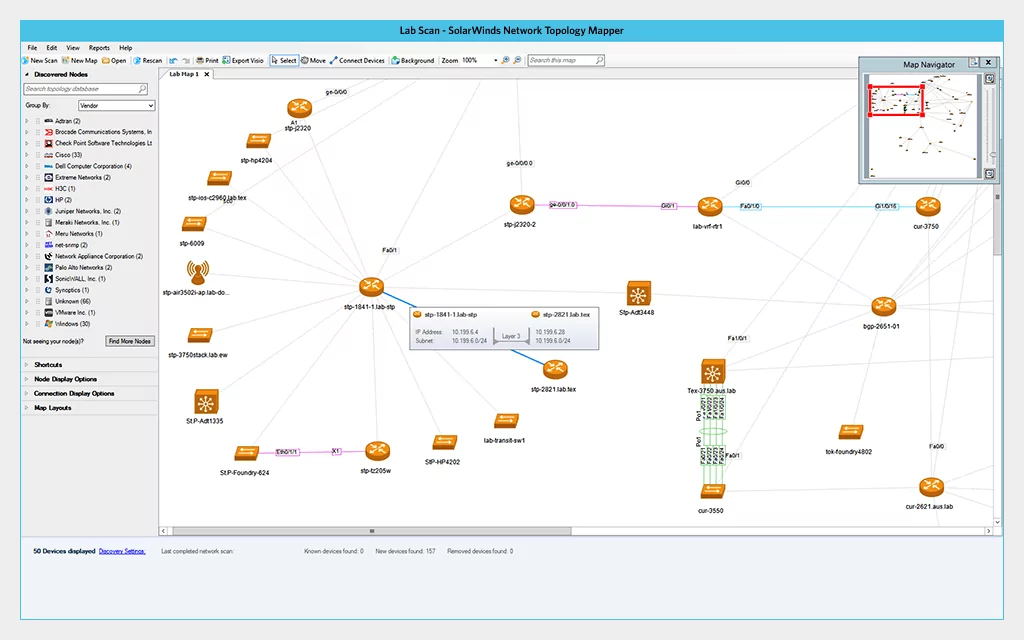
Source: SolarWinds
4. Paessler PRTG Network Monitor

Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is an IT monitoring tool to track the performance and health of networks, servers, applications, and cloud services. It provides insights into IT infrastructure, helping administrators detect issues before they impact business operations.
Key features include:
- Network monitoring: Tracks network devices, applications, databases, and cloud services.
- Integrated monitoring technologies: Supports SNMP, WMI, SSH, packet sniffing, and flow protocols for analysis.
- Maps and dashboards: Visualizes network status with interactive maps and customizable widgets.
- Alerts and notifications: Sends notifications via email, push, or HTTP requests based on predefined conditions.
- Custom sensor support: Allows users to create custom monitoring sensors using REST APIs, SQL queries, and HTTP requests.
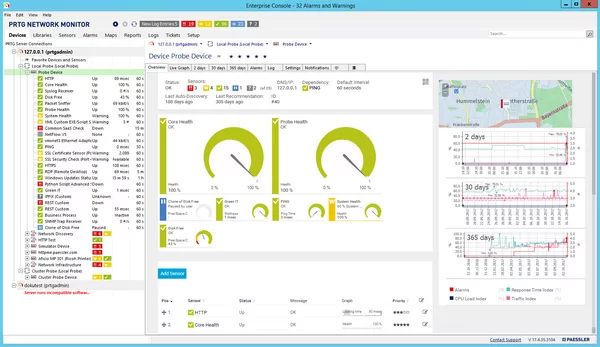
Source: Paessler
5. Device42
Device42 is an IT asset management and dependency mapping tool that provides insights into the relationships between business applications, network components, and services. It helps organizations visualize how infrastructure elements interact across on-premises, cloud, and multi-cloud environments.
Key features include:
- Automated dependency mapping: Identifies and maps relationships between applications, servers, network devices, and cloud resources.
- Business application mapping: Creates visual representations of business applications and their underlying infrastructure.
- Affinity groups and AppFocus filters: Groups related resources for a clearer view of service dependencies and infrastructure interactions.
- Customizable application layouts: Allows users to modify diagrams, add metadata, and define relationships.
- IT Service Management (ITSM) integration: Enables ITSM workflows by visualizing service dependencies and improving incident response.
Source: Device42
6. OpManager Network Mapping
OpManager Network Mapping is a tool to visualize, monitor, and manage IT networks. It discovers network devices, maps physical and virtual connections, and provides insights into infrastructure health.
Key features include:
- Automated network discovery: Scans and maps network devices dynamically.
- Network visualization: Displays device status, traffic flow, and interconnections in an interactive map.
- Layer2 discovery: Automatically maps switches, routers, and connected devices to create topology diagrams.
- Network maps and business views: Groups critical devices and services into customized visual layouts for better monitoring.
- Fault detection and alerts: Highlights faulty devices with color-coded icons and provides notifications.
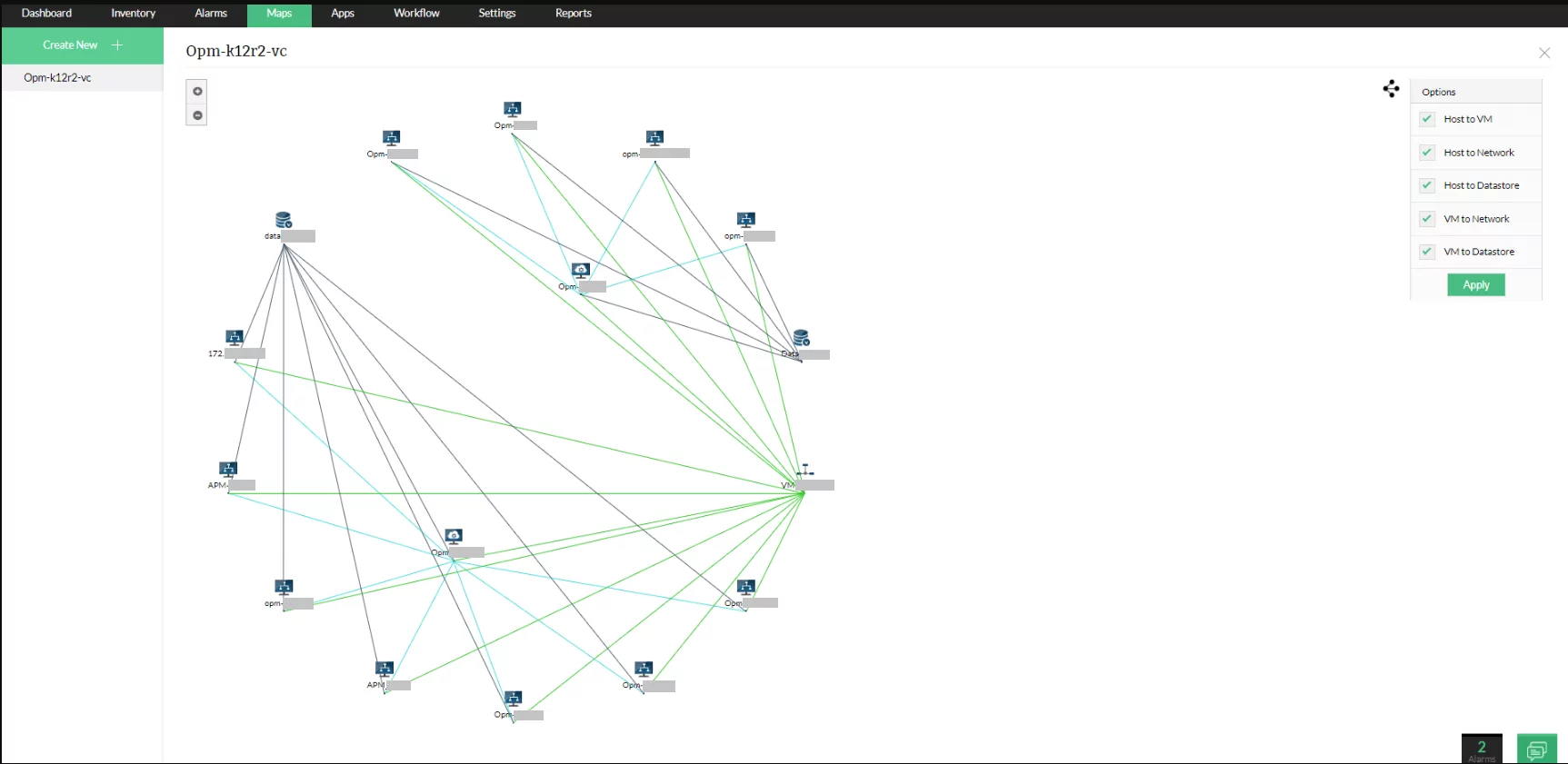
Source: ManageEngine
7. N‑able N-central Network Mapping Software

N‑able N-central Network Mapping Software provides IT professionals and managed service providers (MSPs) with automated network discovery and visualization tools. It maps networks, offering insights into infrastructure layout and connectivity.
Key features include:
- Automated network discovery: Detects new and removed devices, keeping maps up to date.
- Network visualization: Generates topology diagrams to provide an understanding of network structure.
- Troubleshooting: Highlights connectivity issues and performance bottlenecks for problem resolution.
- Scheduled scans: Tracks network modifications without requiring manual intervention.
- Management dashboard: Offers an interface for monitoring and managing multiple client environments.
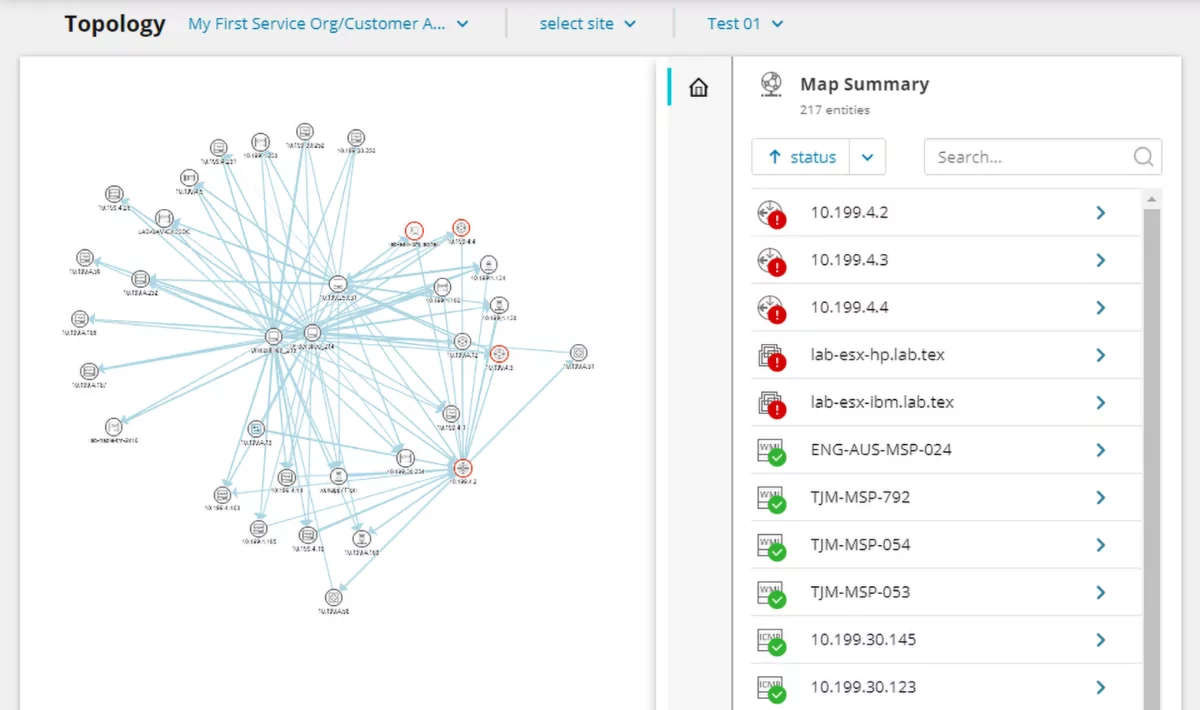
Source: N‑able
8. Intermapper
Intermapper is a network mapping and monitoring tool that provides visibility into IT infrastructure. It discovers devices, creates live network maps, and continuously monitors performance using SNMP and other protocols.
Key features include:
- Automated network discovery: Scans and maps all IP-enabled devices, ensuring up-to-date documentation.
- Network visualization: Displays a color-coded network map with various layouts and customizable icons.
- Monitoring: Continuously tracks devices, interfaces, and applications, providing performance insights.
- Alerts: Sends notifications via text, email, or sound when performance thresholds are exceeded.
- Hierarchical maps: Creates sub-maps to represent different areas, such as buildings, classrooms, or server rooms.
Source: Fortra
Try Faddom’s Network Mapping Feature
We at Faddom, a new IT cloud InfraOps startup, have created a new feature for mapping physical network devices such as switches and routers to troubleshoot problems, analyze the impact of changes, generate documentation, and ensure compliance.
Curious? Just schedule a call with Faddom experts!