What Are Data Center Migration Services?
Data center migration services involve transferring data center assets from one environment to another. This complex process includes moving applications, workloads, and infrastructure. Migration services aim to minimize downtime while ensuring data integrity and security.
These services often use automated tools and professional expertise for a seamless transition. They are useful for organizations looking to improve performance, reduce costs, or adopt new technologies.
Proper data center migration can lead to improved operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Whether migrating to a cloud environment or modernized on-premises systems, data center migration services provide the necessary framework and expertise to make such transitions successful.
Table of Contents
ToggleCloud-Based vs. On-Premise Data Center Migration Tools
Data center migration tools vary based on the target environment—cloud or on-premises. The choice of tools depends on factors like workload complexity, security requirements, and migration scale.
Cloud-Based Migration Tools
Cloud-based migration tools support the transition of workloads and infrastructure to public, private, or hybrid cloud environments. These tools often come with built-in integrations for cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. They offer automated orchestration, dependency mapping, and real-time replication to reduce downtime.
Tools like AWS Application Migration Service and Azure Migrate allow businesses to rehost applications and data with minimal reconfiguration, using features like continuous data replication and test cutovers for validation before go-live. These tools also provide scalability and flexibility, which are especially beneficial for large-scale or multi-region migrations.
They typically include dashboards and reporting features for monitoring progress and identifying bottlenecks. Some cloud-based tools also offer cost estimation and rightsizing capabilities to help organizations optimize cloud spending during and after the migration. Because they operate in the cloud, these tools eliminate the need for additional hardware.
On-Premise Migration Tools
On-premise migration tools focus on moving data center assets between physical locations or from legacy systems to newer on-site infrastructure. These tools are often used when regulatory, security, or latency requirements prevent cloud adoption. They support hardware-based replication, physical-to-virtual (P2V) conversion, and network reconfiguration.
Tools like VMware vMotion allow live migration of virtual machines and continuous data transfer without significant downtime. These tools are especially useful in scenarios involving complex application dependencies, low-latency workloads, or strict compliance mandates.
They provide granular control over each migration step and often include features like rollback capabilities, performance benchmarking, and failover testing. Unlike cloud-based tools, on-premise solutions can be tailored to specialized hardware or network configurations, making them suitable for highly customized or legacy environments.
Learn more in our detailed guide to data center migration tools (coming soon)
Notable Data Center Migration Services and Tools
1. Faddom
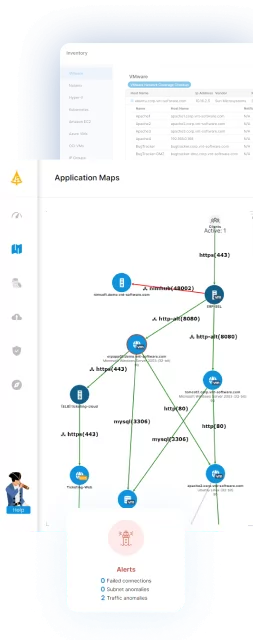
Faddom is a hybrid application dependency mapping platform that simplifies data center migration by providing real-time, visual maps of application and infrastructure dependencies. Designed for fast deployment and deep visibility, Faddom enables organizations to plan and execute migrations confidently, whether moving to the cloud, modernizing on-premises infrastructure, or operating in hybrid environments. It supports a wave-based migration strategy, allowing IT teams to migrate by business applications. This approach reduces risk, maintains uptime, and improves control over the entire migration process.
Deployment model: Hybrid (on-premises and cloud)
Key features include:
- Real-time application dependency mapping: Automatically discovers and visualizes all application and infrastructure dependencies without installing agents or credentials.
- Migration planning and risk mitigation: Maps critical dependencies to prevent service disruptions during and after migration.
- Low-impact deployment: Installs in under 60 minutes with no agents or credentials required, minimizing disruption to ongoing operations.
- Risk assessment and validation: Enables pre-migration risk analysis and post-migration validation by continuously tracking traffic and application performance.
- Rightsizing and resource optimization: Identifies underutilized servers, unnecessary infrastructure, and overprovisioned environments to reduce waste and optimize costs before and after migration.
- Scalability and flexibility: Suitable for organizations of all sizes, with cost-effective pricing and the ability to scale as migration needs to evolve.
- Security and compliance: Since Faddom runs locally, no data leaves the organization, making it ideal for industries with strict data sovereignty or compliance requirements.
Source: Faddom
2. AWS Data Migration Services (DMS)
AWS Data Migration Service (DMS) is a cloud-based tool for migrating databases and data warehouses to AWS or between cloud and on-premises environments. It supports various database types, including relational, NoSQL, and data warehouses. DMS simplifies migration by automating schema conversion, managing replication, and reducing downtime.
Deployment model: Cloud
Key features include:
- Automated schema conversion: Uses AWS DMS Schema Conversion to assess and convert database schemas for compatibility with the target database.
- Continuous data replication: Supports both one-time migrations and ongoing data synchronization between source and target systems.
- Scalability and flexibility: Allows dynamic scaling of migration resources based on workload needs.
- Failover and high availability: Provides automatic failover to backup replication servers to minimize disruptions.
- Source and target support: Enables heterogeneous migrations across different database engines.
Source: Amazon
3. Azure Migrate
Azure Migrate is a service that helps organizations assess, plan, and execute migrations to Microsoft Azure. It provides a centralized platform for discovering workloads, estimating costs, assessing cloud readiness, and migrating various resources, including servers, databases, web applications, and virtual desktops.
Deployment model: Cloud
Key features include:
- Unified migration platform: Offers a single portal for discovery, assessment, and migration of servers, databases, and web apps.
- Workload assessment: Evaluates on-premises workloads for Azure readiness, right-sizing, and cost estimation.
- Business case generation: Estimates total cost of ownership (TCO) and potential savings for migrating to Azure.
- Dependency analysis: Identifies network dependencies between servers to prevent migration issues.
- Flexible Migration options: Supports migrations of VMware and Hyper-V VMs, physical servers, and workloads from other cloud platforms.
Source: Microsoft
4. Google Cloud Migration Center
Google Cloud Migration Center is a centralized hub to help organizations transition their workloads to Google Cloud. It provides assessment, planning, and execution tools. It offers multiple migration strategies, from simple “lift-and-shift” moves to full cloud-native optimizations.
Deployment model: Cloud
Key features include:
- Migration strategies: Supports rehosting, replatforming, refactoring, re-architecting, and rebuilding applications based on business needs.
- Security and compliance: Ensures data protection with Google Cloud’s secure infrastructure, minimizing threats across data centers, hardware, and networks.
- Performance and scalability: Leverages Google Cloud’s infrastructure to provide high availability and cost efficiency for migrated workloads.
- RaMP (Rapid Migration and Modernization Program): Offers guided assessments and insights to simplify the migration process.
- Automated cost assessment: Provides a free migration cost evaluation to help estimate total cost of ownership in Google Cloud.
5. IBM InfoSphere
IBM InfoSphere is a data integration platform to help organizations manage, cleanse, and transform data across multiple environments. It supports massively parallel processing (MPP) for scalable data processing on-premises, in the cloud, or within hybrid environments.
Deployment model: Cloud, on-premises
Key features include:
- Data integration: Provides extract, transform, and load (ETL) capabilities for seamless data movement across systems.
- Data governance and standardization: Helps organizations discover IT assets and define a common business language for data.
- Data quality monitoring: Cleanses and continuously monitors data integrity to improve business insights.
- Scalability with MPP: Enables efficient data processing across large-scale environments.
- Flexible deployment: Supports on-premises, private, public, and hybrid cloud environments, including IBM Cloud Pak for Data.
Source: IBM
6. Talend
Talend is a data integration platform that helps organizations collect, transform, and manage data from multiple sources. It provides a unified approach to data ingestion, transformation, and quality assurance, helping organizations ensure they have reliable and actionable information.
Deployment model: Cloud, on premises
Key features include:
- Universal data integration: Connects virtually any data source to any destination, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
- Flexible deployment: Supports multiple environments, including Apache Spark and cloud platforms, without vendor lock-in.
- Automated data quality: Embeds quality checks at every step to ensure clean, trustworthy data.
- Change data capture (CDC): Enables real-time data replication to keep data fresh and up to date.
- Pipeline designer: Provides a scalable, cloud-native tool for designing and deploying reusable data pipelines.
Source: Talend
7. CloverDX
CloverDX is a data integration platform to simplify complex data migrations with automation, repeatability, and flexibility. It connects to any data source or target, whether on-premises or in the cloud, and enables organizations to build automated workflows. With an iterative approach, CloverDX helps organizations handle large-scale, custom migrations.
Deployment model: Cloud, on-premises
Key features include:
- Data connectivity: Supports any source or target system, including databases, cloud platforms, and custom applications.
- Automation and reusability: Eliminates repetitive tasks with automated workflows, reusable templates, and scalable processes.
- Iterative, repeatable migrations: Adapts to changes in data or requirements without redoing work, ensuring agility in complex projects.
- Automated data validation: Ensures data accuracy and consistency with built-in validation and error-handling mechanisms.
- Transparency and collaboration: Provides user-friendly reporting on migration status and errors for easy stakeholder feedback.
Source: CloverDX
8. SnapLogic
SnapLogic is a data integration and automation platform that enables organizations to connect, transform, and manage data across cloud and on-premises environments. With support for ETL, ELT, and reverse ETL, SnapLogic simplifies data movement while eliminating silos and reducing integration complexity.
Deployment model: Cloud, on-premises
Key features include:
- Data integration: Supports ETL, ELT, and reverse ETL for flexible data movement.
- AI-powered pipeline design: Uses AutoSuggest technology to recommend next steps, reducing manual effort.
- Cloud-native iPaaS: Provides a scalable and agile integration platform for modern data architectures.
- SnapLogic integration catalog: Offers visibility into data pipelines to simplify management and reduce duplication.
- Automated data synchronization: AutoSync enables data ingestion from SaaS applications into cloud data warehouses.
Source: SnapLogic
Related content: Read our guide to data center migration companies (coming soon)
How to Choose Data Center Migration Services
Here are some important considerations for selecting a data center migration service.
1. Determine the Type of Migration Required
Before selecting a migration service, organizations must first define the type of migration they need. There are several common migration strategies:
- Rehosting (lift-and-shift): Moving applications and workloads to a new environment with minimal changes. This is the fastest and simplest migration approach but may not take full advantage of cloud-native features.
- Re-platforming: Making slight optimizations to applications while moving them to a new infrastructure. This balances speed with performance improvements.
- Re-architecting: Completely redesigning applications to fully leverage the capabilities of the target environment (such as cloud-native scalability). While this requires more effort, it often results in significant long-term benefits.
- Hybrid migrations: Combining multiple migration approaches, such as keeping some workloads on-premises while moving others to the cloud.
2. Evaluate Service Provider Expertise
Not all migration service providers are created equal. The expertise and experience of a provider can significantly impact the success of a migration. Key factors to evaluate include:
- Track record: Look for case studies, references, and testimonials that demonstrate successful migrations similar to the organization’s requirements.
- Certifications: Ensure the provider has certifications from relevant cloud or infrastructure vendors (such as AWS Certified Migration Competency or Microsoft Azure Expert MSP).
- Industry-specific knowledge: If the organization operates in a regulated industry (finance, healthcare, government, etc.), ensure the provider has expertise in handling compliance, data security, and regulatory requirements.
- Support and SLAs: Check for service-level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee minimal downtime, fast issue resolution, and 24/7 support.
3. Analyze Tools and Methodologies
The tools and methodologies used by a migration service provider can determine the efficiency and reliability of the migration process. Organizations should evaluate the following factors:
- Automation capabilities: Automated discovery, dependency mapping, and workload replication reduce manual effort and minimize migration errors.
- Migration strategy support: Does the provider offer support for lift-and-shift, re-platforming, or full re-architecting? Having a flexible approach ensures compatibility with business goals.
- Performance monitoring and testing: Look for tools that enable real-time tracking of migration progress, pre-migration testing, and post-migration validation to detect potential issues early.
- Integration with existing infrastructure: Some tools support specific cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) or hybrid environments better than others. Ensuring compatibility reduces post-migration complications.
4. Assess Cost Implications
Migration costs can vary based on workload complexity, data volume, and the level of customization required. A thorough cost assessment should include:
- Upfront vs. ongoing costs: Some services have one-time migration fees, while others operate on a subscription or pay-as-you-go model. Understanding the pricing structure helps in budget planning.
- Hidden costs: Licensing fees, additional storage, extended support, and post-migration optimization services can add unexpected expenses. Ensure all potential costs are accounted for.
- Cost estimation tools: Many providers offer calculators to estimate total cost of ownership (TCO) before migration. These tools help compare different service providers based on long-term financial impact.
- Downtime and productivity losses: A poorly planned migration can lead to unexpected downtime, affecting business operations and revenue. Evaluating potential productivity losses alongside service costs is essential.
5. Consider Scalability and Flexibility
A migration service should not only meet current needs but also accommodate future growth. Key considerations include:
- Scalability of infrastructure: Whether moving to a cloud or hybrid environment, the new infrastructure should support workload expansion without requiring a major overhaul.
- Flexible deployment options: Some migration services provide more adaptability in supporting on-premises, cloud, or multi-cloud environments. Ensuring flexibility prevents vendor lock-in and allows for future adjustments.
- Ongoing optimization: Some services include performance monitoring, auto-scaling, and cost optimization tools to adjust resources based on workload demands.
- Disaster recovery and redundancy: Ensuring that the migration service includes backup and failover options helps prevent data loss and ensures business continuity.
Conclusion
Selecting the right data center migration service involves balancing technical requirements, budget constraints, and long-term infrastructure goals. The best tools and services provide automation, flexibility, and robust support for various migration strategies, from simple lift-and-shift to full re-architecture. By carefully evaluating provider expertise, tool capabilities, and cost implications, organizations can reduce risk, minimize downtime, and ensure a smooth transition that supports ongoing digital transformation.