What Is VMware Migration to Azure?
VMware migration to Azure refers to the process of moving on-premises VMware virtual machines (VMs) to Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform. This migration enables businesses to leverage Azure’s cloud capabilities without having to rebuild their VMs from scratch. The process involves various steps, including assessment, planning, replication, and cutover, to ensure a smooth transition from the VMware environment to Azure.
The goals of VMware migration to Azure are typically cost efficiency, flexibility, and enhanced performance. By migrating VMs to Azure, organizations can benefit from Azure’s scalable infrastructure, reduce their data center footprint, and optimize IT resources management. This migration supports various scenarios such as disaster recovery, application modernization, and data center exit strategies.
This is part of a series of articles about Application Migration
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Are Companies Considering Migrating from VMware?
The decision to migrate from VMware to alternative virtualization platforms is increasingly prevalent among businesses, influenced by various strategic, economic, and technological factors. One primary motivator is cost. The shift from VMware’s perpetual license model to a subscription-based model under Broadcom’s acquisition has significantly increased expenses for many organizations. This change, coupled with altered billing practices and restricted direct purchase options for smaller customers, has made alternative solutions more financially appealing, particularly for companies aiming to manage and reduce their total cost of ownership effectively.
Flexibility and scalability also drive the migration decision. Alternative virtualization platforms often provide superior flexibility, crucial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or undergoing frequent changes in IT demands. These platforms allow for swift adaptation of IT resources without substantial additional costs, a critical advantage over more rigid systems.
Additionally, the migration towards environments supporting open standards enhances interoperability and compatibility with various systems and applications. This is particularly beneficial in diverse IT environments where seamless integration across different platforms is essential.
Related content: Read our guide to VMware to Nutanix migration
Benefits of Migrating from VMware to Azure
Beyond the financial concerns raised by VMware’s acquisition, here are several key benefits of migrating from VMware to Azure:
- Dynamic scalability: In the Azure cloud, businesses can easily scale up or down based on their needs without worrying about physical hardware limitations. This scalability ensures that resources are efficiently matched with demand, optimizing costs and enhancing performance. Azure’s auto-scaling capabilities allow for automatic adjustment of resources during peak times.
- Integration with Microsoft ecosystem: Migrating to Azure provides seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, including Office 365, Dynamics 365, and Power Platform. This allows businesses to leverage their existing Microsoft investments and streamline workflows. Additionally, Azure offers robust developer tools and services that facilitate application development and management.
- Security and compliance: Azure provides comprehensive security features, including threat protection, encryption, and identity management, to safeguard data and applications. Furthermore, Azure meets a broad set of international and industry-specific compliance standards.
- Extensive global network: Azure’s global footprint ensures high availability and low-latency access to applications and data. With data centers in more regions than any other cloud provider, Azure enables businesses to deploy their applications close to their users, improving performance and user experience.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you optimize VMware to Azure migrations:
-
Select the right migration approach
Use agentless or agent-based methods based on your requirements. Agentless is simpler, while agent-based offers more control and options.
-
Prepare for post-migration security
Implement Just in Time (JIT) access control and configure Network Security Groups (NSGs) to protect management endpoints.
-
Review and adjust disk caching settings
Tailor caching options for better performance based on workload requirements.
-
Utilize Azure Update Management
Automate updates to maintain security and performance post-migration.
-
Monitor and optimize cloud costs
Use Azure Cost Management to track usage and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Options to Migrate from VMware to Azure
Migrate VMware VMs to Azure (Agentless)
Migrating VMware VMs to Azure through an agentless method is a straightforward approach that minimizes disruption. This method involves using Azure Migrate, a central hub that assesses, replicates, and migrates VMs to Azure. The agentless migration does not require installing anything on the VMs, making it simpler and reducing the risk of compatibility issues.
The process includes continuous replication of VMs to Azure, ensuring that the transition is seamless and that data is synchronized. Once the migration is complete, VMs can be tested in Azure without affecting the production environment, providing confidence in the migration outcome.
Learn more in AWS documentation
Migrate VMware vSphere VMs to Azure (Agent-Based)
An agent-based migration of VMware vSphere VMs to Azure involves installing agents on the VMs to facilitate the migration process. This approach provides more granular control over the migration and allows for advanced features, such as application consistency snapshots and multi-tier application support.
While this method is more complex due to agent installation, it provides a high degree of customization, catering to complex migration scenarios. Businesses can benefit from detailed monitoring and reporting, ensuring a comprehensive view of the migration process and enabling informed decision-making.
Learn more in AWS documentation
Migrate VMware VMs to Azure with PowerShell (Agentless)
Migrating VMware VMs to Azure using PowerShell provides a script-based, agentless approach, offering automation and flexibility. PowerShell scripts automate the assessment, replication, and cutover phases, streamlining the migration process. This method is ideal for businesses with specific automation needs or those looking to integrate migration steps into existing deployment processes.
Through PowerShell, businesses can customize their migration workflows, incorporating unique requirements and ensuring that the migration aligns with their operational practices. This customizable approach provides a high level of control, enabling efficient and tailored migrations.
Learn more in AWS documentation
VMware to Azure: Best Practices for Post Migration
Map all your VMWare instances to Ensure You Didn’t Leave Any Behind
After completing a migration from VMware to Azure, it’s crucial to ensure that all virtual machines (VMs) intended for migration have successfully moved to the Azure environment. This verification process involves conducting a comprehensive inventory of all VMware instances both before and after migration. Mapping each VM ensures that none are inadvertently left behind, which could result in operational disruptions or data loss.
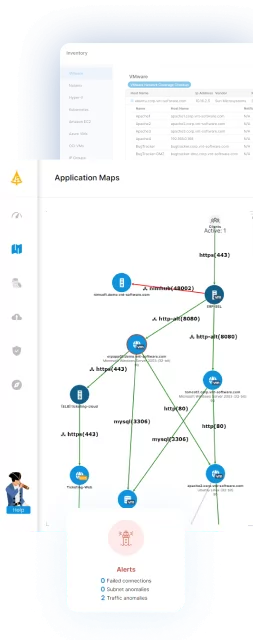
Automate VMware asset mapping with Faddom
Faddom is an application dependency mapping tool that can automatically scan your VMware assets, provide detailed insights and visualizations of your on-premise and cloud infrastructure, and show discrepancies between your planned and actual migration outcomes.
Faddom can not only prepare a full inventory of your VMs, but also ensure that each VM’s dependencies and configurations, such as CPU, memory, and disk allocations, match your records.
Faddom is agentless, doesn’t require credentials, and inexpensive, starting at $10K/year. It updates 24/7, and is fast to operate: one person can map the entire organization in an hour.
Learn more about Faddom for data center migration!
Use Just in Time (JIT) VM Access Control
Integrating Just in Time (JIT) VM Access Control improves security of your VMs in Azure. This approach limits the window of opportunity for attacks by controlling inbound traffic, allowing administrative access to VMs only when necessary and for strictly defined periods. Setting up
JIT access through Azure Security Center ensures that VM access is granted promptly and securely, minimizing the risk of breaches. Adopting JIT VM Access Control also simplifies management of access permissions. It eliminates the need for permanent open ports, reducing the risk of exploitation.
Review and Adjust Data Disk Caching
After transitioning VMware VMs to Azure, an essential step is to reassess and fine-tune the caching settings of your data disks, tailoring them to the specific demands of your applications.
Azure’s disk caching offers three settings: None, ReadOnly, and ReadWrite. Each serves different purposes—ReadOnly is ideal for enhancing performance in read-heavy operations, while the None option should be chosen for workloads that don’t benefit from caching, eliminating unnecessary performance overhead. Properly aligning your disk caching strategy with the nature of your workload can lead to marked improvements in application performance.
In optimizing disk performance, understanding the characteristics of your applications is key. For instance, applications that frequently read the same data can significantly benefit from setting the cache to ReadOnly, as it reduces latency and increases throughput. On the other hand, applications that primarily write data or have minimal repeat reads might perform better with caching disabled.
Implement NSGs to Restrict Network Traffic to Management Endpoints
Post-migration, employing Network Security Groups (NSGs) is a vital measure to safeguard your Azure deployments. NSGs act as a firewall for your VMs and other Azure resources, enabling you to define rules that allow or block network traffic. Specifically, configuring NSGs to restrict access to management endpoints (such as SSH and RDP) is a prudent step.
By setting strict rules that only permit access from approved IP addresses or ranges, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access and potential security incidents.
Utilize Azure Update Manager
Azure Update Management emerges as a crucial tool in maintaining the security and reliability of your VMs post-migration. This service automates the process of applying updates across your VM fleet, enabling you to schedule and manage updates with ease. With Azure Update Management, you can ensure that your VMs are always up to date with the latest security patches and performance improvements.
The centralized management feature of Azure Update Management provides a comprehensive view of your update status across all VMs, simplifying the tracking of pending and completed updates. By planning update deployments during low-usage periods, you can minimize the impact on your operations, ensuring that your services remain available and performant.
Implement Azure Cost Management
After moving to Azure, it’s important to actively manage and optimize your cloud spend to avoid unnecessary expenses. Azure Cost Management is a free tool that offers deep insights into your cloud usage and expenditures. It enables you to monitor your spending closely, set up budgets, and receive alerts to avoid cost overruns.
With Azure Cost Management, you can identify underutilized resources that can be downsized or eliminated, optimizing your cloud costs without compromising on performance or capability. By analyzing spending trends and utilizing the tool’s recommendations, you can adjust your cloud strategy to align with your budgetary constraints and operational objectives.
Conclusion
Migrating VMware workloads to Azure offers substantial benefits, including cost efficiency, dynamic scalability, and enhanced security. By leveraging Azure’s ecosystem, organizations can integrate with existing Microsoft products and services, optimizing their IT operations. Post-migration, it’s important to adopt best practices such as utilizing Just in Time (JIT) access, configuring Network Security Groups (NSGs), and implementing Azure Cost Management to ensure a secure, efficient, and cost-effective cloud environment. Properly managed, VMware migration to Azure can significantly transform your IT infrastructure, driving greater flexibility and innovation.
Learn more about Faddom for data center migration or start a free trial by filling out the form on the sidebar!