What Are Application Migration Services?
Application migration services help organizations move software applications from one environment to another. This could involve transitioning from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, moving between cloud providers, or shifting from one data center to another. The goal is to preserve application functionality while improving scalability, performance, or cost-efficiency.
These services include tools and processes to assess existing environments, replicate workloads, and reconfigure systems for compatibility in the new environment. They reduce the risk and complexity of migrations, providing automation, monitoring, and support throughout the transition.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Features of Application Migration Services
Automated Replication
Automated replication simplifies the migration process by continuously copying application data, configurations, and system states from the source environment to the destination. This is typically done using agents or lightweight tools that run on the source machines and handle the replication without needing manual coordination.
By automating these tasks, organizations can avoid the complexity of scripting or manually transferring files, reducing the likelihood of errors or missed dependencies. It also allows migrations to proceed in the background with minimal disruption to production systems.
Additionally, automated replication is often designed to be application-agnostic.
Incremental Replication
Incremental replication improves the efficiency of data transfer by sending only the changes made since the last synchronization. This is especially important in large-scale environments where transferring entire workloads repeatedly would be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
With incremental updates, organizations can keep the destination environment closely aligned with the source while minimizing bandwidth usage and reducing the total time required for final cutover. It also supports near-zero-downtime migrations, since the system can remain operational until just before the switch is made.
Most solutions include mechanisms to track file changes, database transactions, or block-level differences, ensuring precise and consistent updates without full data duplication.
Support for Diverse Source Environments
Effective application migration services are designed to handle a broad array of infrastructure types and configurations. This includes support for physical servers, on-premises virtual machines (e.g., VMware, Hyper-V), legacy platforms, and different operating systems such as Windows and Linux.
In heterogeneous environments, this allows enterprises to consolidate or modernize applications without major rewrites. It also enables phased or hybrid migration strategies where only part of the infrastructure is moved initially. Many tools include compatibility layers or conversion utilities to adapt workloads to the target platform.
Built-in Monitoring and Management
Built-in monitoring capabilities allow teams to track every stage of the migration process through centralized dashboards and real-time metrics. These tools provide visibility into replication status, data transfer speeds, error logs, and resource utilization.
Management features often include the ability to start, pause, or resume migrations; set up alerts for failed tasks or threshold violations; and generate reports for auditing and compliance. This makes it easier to coordinate large-scale migrations involving multiple systems or applications.
Post-Migration Optimization
After applications have been migrated, optimization tools help align them with the target environment’s best practices. This can include resizing compute resources to better fit actual usage patterns, reconfiguring network settings, and replacing legacy components with cloud-native services for improved scalability or cost-efficiency.
Optimization also involves performance tuning, such as adjusting database indexes, upgrading dependencies, or improving security configurations to match the target platform’s capabilities. In cloud migrations, tools may recommend autoscaling policies, storage tiering, or load balancing adjustments.
Notable Application Migration Services and Tools
1. Faddom
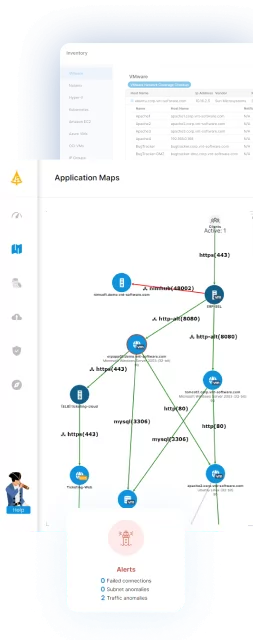
Faddom is a lightweight, agentless application dependency mapping solution that supports seamless migration planning across hybrid environments. Unlike traditional tools, Faddom passively discovers and maps application and infrastructure dependencies in real-time without needing credentials, agents, or active scanning.
Key features include:
- Real-Time Dependency Mapping: Automatically maps every server, connection, and dependency in your hybrid environment, ensuring complete visibility.
- Quick Deployment: Install in under 60 minutes and get instant visibility.
- Wave-Based Migration Strategy: Faddom facilitates wave-based migration by real-time mapping of dependencies and grouping assets into business applications. This allows teams to migrate seamlessly while minimizing disruptions to business operations.
- Change Management: Tracks infrastructure and communication changes to validate pre and post-migration environments, ensuring continuity and reducing cutover risk.
- Optimized Resource Planning: Enables precise rightsizing and helps eliminate unused or redundant infrastructure, cutting unnecessary costs.
- Multi-Purpose Use: Beyond migration, it supports cybersecurity, change management, documentation, discovery, and compliance initiatives, all from a single deployment.
Source: Faddom
2. AWS Application Migration Services
AWS Application Migration Service is a fully managed tool that enables organizations to move on-premises or cloud-based applications to AWS. It automates the replication of servers, including applications, system configurations, and data, without requiring changes to the source environment.
Key features include:
- Source environment support: Migrates applications from physical servers, VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, or other on-premises and cloud infrastructures.
- Application modernization: Allows users to apply built-in or custom modernization actions, such as OS upgrades, SQL license conversion, or disaster recovery setup.
- Low disruption migrations: Maintains normal operations throughout replication, with minimal downtime during cutover.
- Cross-region and cross-account migrations: Moves workloads across AWS Regions, Availability Zones, or accounts.
Source: Amazon
3. Azure Migrate
Azure Migrate is a centralized platform that helps organizations discover, assess, and move on-premises workloads to the Azure cloud. It supports a range of assets, including servers, databases, web applications, and virtual desktops. It also supports modernization by enabling upgrades and replatforming during the migration process.
Key features include:
- Discovery and assessment: Offers an appliance or lets users import inventory data to identify workloads. Helps assess Azure readiness, generate business cases, and estimate costs and savings of migrating.
- Unified migration hub: Provides access to discovery, assessment, migration, and modernization tools from a single portal.
- Dependency analysis: Helps understand application dependencies and network connections between servers.
- Migration methods: Supports agentless or agent-based migration of VMware, Hyper-V, physical servers, and workloads from other clouds.
- Workload modernization: Helps migrate and modernize SQL Server databases and ASP.NET web apps, targeting Azure-native services like Azure SQL Managed Instance or Azure App Service.
Source: Microsoft
4. Google Cloud Migration Center
Google Cloud Migration Center is a platform to manage the cloud migration. It helps organizations move from on-premises or other cloud environments to Google Cloud with automated asset discovery, infrastructure assessment, cost estimation, and migration planning.
Key features include:
- Cloud cost estimation: Generates quick estimates of future Google Cloud costs using configuration and sizing data from existing infrastructure (currently in preview).
- Automated asset discovery: Scans the on-premises environment to build an inventory of assets, including servers and databases.
- Infrastructure assessment: Analyzes workloads to determine total cost of ownership, helping assess technical fit for Google Cloud products.
- Migration planning tools: Insights from assessments help users to build migration plans based on business constraints and technical requirements.
- Flexible migration execution: Provides tools to support various migration strategies, including lift-and-shift (rehost), platform optimization (replatform), and code-level changes (refactor).
Source: Google Cloud
5. VMware HCX
VMware HCX is a hybrid cloud mobility platform that simplifies and automates the migration of workloads across VMware and non-VMware environments. It supports large-scale, high-performance migrations between on-premises data centers and public cloud platforms, including VMware Cloud on AWS, Azure VMware Solution, and Google Cloud VMware Engine.
Key features include:
- Workload mobility: Migrates workloads across a range of VMware platforms and vSphere versions (6.5+).
- Migration methods: Supports multiple migration types, including bulk migration and zero-downtime HCX vMotion.
- Hybrid networking: Leverages VMware NSX to automate routing and ensure secure connectivity between source and target environments.
- Support for non-vSphere VMs: Uses OS-Assisted Migration (OSAM) to move workloads from non-vSphere environments into vSphere-based destinations.
- Operational continuity and rebalancing: Rebalances workloads to meet scaling, compliance, or cost objectives.
Source: VMware
6. OpenText Migrate
OpenText Migrate is a migration platform to move workloads across physical, virtual, and cloud environments. It enables secure, low-downtime migrations for data center consolidation, hardware upgrades, cloud adoption, and post-merger integration.
Key features include:
- Any-to-any migration: Migrates workloads between physical, virtual, and cloud platforms—including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Full-server or data-only migrations: Supports entire server migrations or targeted data transfers.
- Automated management console: Helps simplify configuration and execution with a centralized interface for task orchestration and error reduction.
- Continuous replication: Helps keep source and destination environments synchronized during migration.
- Testing and cutover: Enables pre-cutover testing and automated switchover.
7. Cloudsfer
Cloudsfer is a data migration platform that enables movement of content between on-premise systems and over 30 supported cloud services. It offers automated tools that preserve metadata, permissions, and structure, while simplifying complex transfers from legacy enterprise content management (ECM) systems or modern cloud platforms.
Key features include:
- Cloud-to-cloud migration: Moves data between over 20 supported cloud platforms—including Microsoft 365, Dropbox, Box, Google Drive, and S3.
- Multi-user migration: Can transfer multiple user accounts in bulk.
- On-premise to cloud: Migrates data from file systems or ECM platforms like Documentum, LiveLink, FileNet, and Lotus Notes to cloud targets such as SharePoint Online, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams.
- Cloud-to-on-premise migration: Automates cloud data exports to local environments or NAS systems using script-free processes.
- On-premise to on-premise transfers: Supports migrations between internal systems or from legacy ECM platforms to SharePoint Server.
Source: Cloudsfer
8. Dynatrace
Dynatrace is a software intelligence platform that supports cloud migration and post-migration operations. By delivering deep observability, real-time dependency mapping, and AI-driven analytics, it helps organizations to reduce risk, accelerate migration timelines, and ensure application performance.
Key features include:
- Automated dependency mapping: Visualizes the environment using Smartscape to map infrastructure, applications, and services.
- Migration readiness assessment: Offers insights into current workloads, usage patterns, and architectural dependencies.
- Performance baselines and monitoring: Compares before-and-after metrics to identify performance regressions and ensure consistent service quality throughout the migration.
- Root cause analysis with causal AI: Helps detect and resolve performance or availability issues using an AI engine.
- Security vulnerability detection: Helps identify and remediate potential risks during migration to prevent security gaps in the new environment.
Source: Dynatrace
Learn more in our detailed guide to application migration tools
Conclusion
Application migration services simplify the complexity of transitioning workloads by offering automation, compatibility support, and post-migration optimization. However, not all solutions provide real-time visibility into dependencies, agentless deployment, or change management out of the box. The best tools provide a complete map of your hybrid infrastructure in minutes, helping reduce risk, prevent overspending, and support long-term modernization not just during the migration but also after it’s complete. Look for a platform that delivers accurate, continuous mapping without disrupting your systems.
Discover more about Data Center Migration with Faddom