What Is VMware?
Launched in 1998 as a virtualization platform, VMware has gained a dominant position in enterprise environments. One of its primary advantages is that it enables multiple virtual machines (VMs) to operate on a single physical server, reducing hardware costs and increasing efficiency. The platform also offers advanced features like live migration, high availability, and disaster recovery.
Compared to other virtualization platforms, VMware is renowned for its dependability and stability. It also offers a vast ecosystem of partners and integrations, making it a flexible option for organizations of all sizes. Nonetheless, it may not be the best option for all companies, as it requires specialized hardware and comes with a rather high licensing fee. Yet VMware has many applications across multiple sectors, including healthcare, finance, and government—where security and compliance are paramount.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Nutanix?
Introduced in 2009, Nutanix is a hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) platform that merges computing, storage, and networking into a single appliance, thus making it a simpler and more cost-effective option for IT operations. The platform boasts advanced features like automation, self-healing, and machine learning—adding value to its already impressive offering.
When compared to other HCI platforms, Nutanix stands out for its scalability and user friendliness. It also has a built-in hypervisor that reduces the need for specialized hardware. However, it is essential to note some downsides to using Nutanix, such as its higher upfront costs and the requirement for specialized skills to manage it. Nonetheless, Nutanix has an extensive range of applications across many industries, including education, media, and retail—where agility and flexibility are critical factors for success.
This is part of a series of articles about Nutanix.
Nutanix vs. VMware: 5 Key Differences and How to Choose
Nutanix competitors are numerous, but this section provides a detailed comparison between VMware and Nutanix across various fronts.
1. Architecture, Scalability, and Management
VMware and Nutanix have different architectures, with VMware relying on a virtualization layer and Nutanix operating as a hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) platform. VMware provides a more traditional virtualization approach, while Nutanix’s HCI approach provides a more streamlined and integrated infrastructure. In terms of scalability, both platforms are scalable, but Nutanix is considered more flexible in terms of hardware and storage management.As for management, VMware’s vCenter provides a centralized management console for virtualization management. Nutanix’s Prism management interface, on the other hand, provides a unified management interface for all infrastructure components.
2. Licensing and Pricing Models
VMware’s licensing and pricing models vary based on the product and features used. VMware offers different licensing schemes such as per-CPU, per-VM, and subscription-based models, which may be more suited for larger enterprises due to their flexibility. The per-CPU core licensing model requires licensing for at least 16 cores per CPU, while the per-VM model charges based on the number of virtual machines. VMware’s vSphere, vCenter, vSAN, and NSX all follow these varied licensing structures.
Nutanix offers a more predictable node-based licensing model. Each node in a Nutanix cluster is licensed regardless of the number of processors or cores. Nutanix also provides capacity-based licensing and subscription options to further increase flexibility. This model can be particularly advantageous for smaller organizations or those with limited IT resources, as it reduces the administrative burden.
3. Performance and Efficiency
VMware ESXi is a mature hypervisor known for its power and efficiency in handling a range of workloads. VMware’s advanced resource management features like Storage DRS and Network I/O Control optimize performance based on workload requirements, making it suitable for environments with diverse and demanding applications.
Nutanix, built on a hyper-converged infrastructure, integrates compute, storage, and virtualization resources into a single system. This architecture can provide performance benefits, particularly in data-intensive applications, by ensuring data locality—keeping data close to the VM that uses it. Nutanix’s Acropolis Operating System and AHV hypervisor work seamlessly within this environment.
4. Integration and Compatibility
VMware’s broad ecosystem and extensive partner network are significant advantages. VMware supports a range of hardware, operating systems, and third-party applications, making it suitable for diverse IT environments. Its strong cloud integration capabilities with major providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud enhance its appeal for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
Nutanix, while focusing on hyper-converged infrastructure, also offers strong integration capabilities. Nutanix supports multiple hypervisors, including VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V, providing flexibility for organizations with existing virtualization investments. Nutanix’s Prism management interface simplifies operations across the integrated stack, ensuring compatibility with a variety of applications and cloud services. However, its smaller ecosystem of third-party add-ons compared to VMware may limit some integration options.
5. Deployment and Configuration
VMware vSphere, combined with its vSAN solution, offers a high degree of customization but can be complex to deploy, especially for those unfamiliar with VMware products. While VMware Cloud Foundation provides a more integrated experience, initial setup can still be complex.
Nutanix is often noted for its simplicity and ease of deployment. Its out-of-the-box readiness for many use cases and automated discovery and clustering capabilities make it a user-friendly option. Nutanix’s Prism interface further simplifies deployment tasks, making it accessible even for users with limited technical expertise. This ease of use can lead to quicker time-to-value and lower administrative overhead.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you choose between Nutanix and VMware effectively:
-
Align platform with workload needs
VMware is well-suited for traditional enterprise applications, while Nutanix is optimized for cloud-native and hyper-converged environments, making it ideal for modern, scalable workloads.
-
Consider management complexity
Nutanix’s Prism offers an intuitive, unified management interface that reduces the need for specialized expertise. VMware’s vCenter, while more powerful, can be complex and may require more training and support.
-
Plan for future scalability
Nutanix allows easy scaling by adding nodes with minimal disruption. VMware may involve more planning and configuration to scale effectively, particularly in diverse environments.
-
Analyze total cost of ownership
VMware’s complex licensing and hardware requirements can lead to higher TCO. Nutanix’s simpler, node-based licensing may offer cost savings, especially for organizations with limited IT resources.
-
Evaluate integration capabilities
VMware has a broad ecosystem with extensive third-party integrations, making it versatile for complex IT landscapes. Nutanix, though flexible, might have fewer integration options, particularly with older or niche systems.
Nutanix Pros and Cons
Nutanix pros:
- Simplified management: Nutanix’s Prism interface offers a unified and intuitive management experience, reducing the need for specialized expertise.
- Scalability: Nutanix’s HCI architecture allows for seamless scaling by adding nodes, making it adaptable to changing business needs.
- Performance: Nutanix AHV hypervisor is optimized for performance with features like data locality, which keeps data close to the VMs that use it.
- Cost efficiency: With a node-based licensing model, Nutanix can be more cost-effective, particularly for smaller organizations.
- Flexibility: Support for multiple hypervisors, including AHV, ESXi, and Hyper-V, provides deployment flexibility.
Nutanix cons:
- Limited ecosystem: Compared to VMware, Nutanix has a smaller ecosystem of third-party integrations, which might limit options for some users.
- Higher upfront costs: Initial investment in Nutanix hardware and software can be higher, which might be a barrier for some organizations.
- Specialized skills: While management is simplified, initial setup and advanced features might require specialized skills.
- Hardware compatibility: Nutanix AHV has limitations in terms of supported hardware, which might restrict certain configurations.
VMware Pros and Cons
VMware pros:
- Mature ecosystem: VMware has a well-established ecosystem with extensive third-party integrations and support.
- Advanced features: The platform includes advanced features like vMotion, HA, and DRS, which enhance performance and reliability.
- Compatibility: It offers broad compatibility with a range of hardware, operating systems, and applications.
- Comprehensive management: vCenter provides management tools that are suitable for complex environments.
- Cloud integration: It has strong partnerships with major cloud providers, enabling hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
VMware cons:
- Complex licensing: VMware’s licensing can be complicated and potentially costly, especially for smaller organizations.
- Higher TCO: Total cost of ownership can be higher due to licensing fees, hardware requirements, and management overhead.
- Complex deployment: Initial setup and configuration can be complex and may require specialized knowledge.
- Vendor lock-in: Dependency on VMware’s ecosystem can result in vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility for future changes.
Furthermore, the semiconductor company Broadcom has acquired VMware, and many in the industry are concerned this could lead to reduced choice, higher prices, and possibly significant changes to the product offering and roadmap of VMware. In a time of such uncertainty, Nutanix promises a risk-free alternative.
Nutanix vs. VMware: How to Choose?
When choosing between VMware and Nutanix, IT managers should consider several factors, including:
- Workload requirements: Different workloads may perform better on different platforms, so IT managers should evaluate which platform is best suited for their specific workload requirements.
- Budget: VMware and Nutanix have different licensing and pricing models, so IT managers should evaluate which platform fits within their budget.
- Management overhead: VMware and Nutanix have different management interfaces, so IT managers should evaluate which platform provides the most streamlined management experience for their organization.
- Integration with other infrastructure components: IT managers should evaluate which platform integrates better with their existing infrastructure components, such as storage and networking.
Comparing VMware and Nutanix
The table below provides a high-level overview of the differences between VMware and Nutanix:
| Key Factor | VMware | Nutanix |
| Architecture | Traditional virtualization | Hyper-converged infrastructure |
| Scalability | Limited to individual physical servers | More scalable, built-in clustering |
| Management | Comprehensive management suite | Streamlined an simplified interface |
| Licensing | Traditional licensing model | Flexible and subscription-based model |
| Pricing | Higher upfront costs, long-term savings | Lower upfront costs, potential long-term costs |
| Performance | Proven performance, but not as optimized for HCI | More optimized for HCI |
| Security | Strong security features | Strong security features |
| Integration | Broad integration capabilities | Tighter integration of hardware and software |
| Use Cases | Established enterprise workloads | Modern and cloud-native workloads |
| Pros | Established market presence, comprehensive management suite, proven performance |
More scalable and streamlined, flexible licensing and pricing, optimized for HCI |
| Cons | Limited scalability, complex management, higher upfront costs | Less established, potential long-term costs, may not be optimal for legacy workloads |
Both platforms have their advantages and disadvantages, so the choice ultimately depends on the unique needs of the organization. However, if scalability and simplicity are the main considerations, Nutanix may be the better choice. If legacy systems and a more established platform are important, VMware may be the best option.
Say Hello to Faddom
The virtualization and HCI market is constantly evolving, and new trends such as hybrid and multi-cloud environments, containerization, and edge computing are emerging. VMware and Nutanix are adapting their offerings to meet the new demands of these trends. It is important for IT managers to stay up-to-date with these changes and assess how these platforms can benefit clients’ organizations.
Both VMware and Nutanix are robust virtualization and HCI platforms with unique strengths and weaknesses. IT managers should thoroughly assess their specific needs to determine which platform is the best fit for their organization. As the virtualization and HCI market continues to evolve, VMware and Nutanix will continue to adapt to meet the demands of a constantly changing IT landscape.
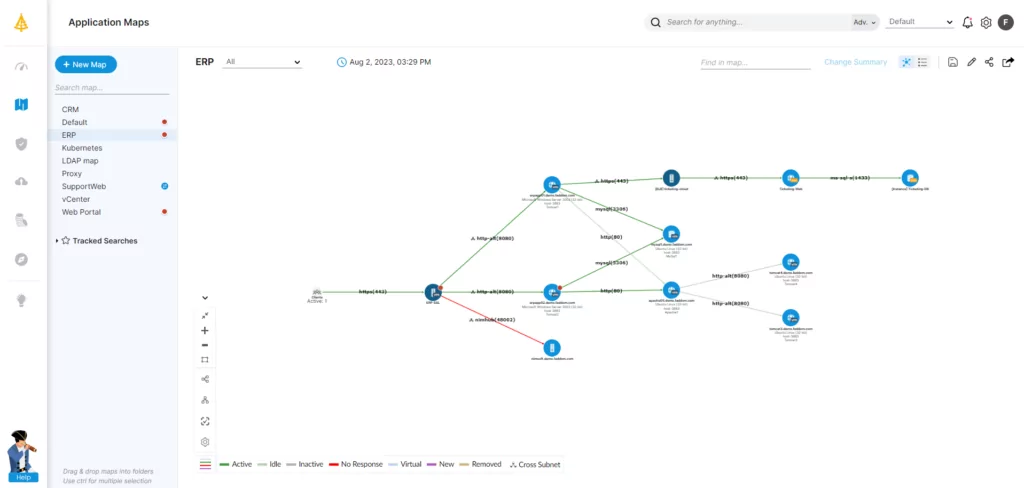
Whether you use VMware or Nutanix, Faddom helps you visualize your entire on-premise and cloud infrastructure with continuous, automatic updates — in as little as 60 minutes and without using agents.
Check it out for yourself and start a free trial today by filling out the form in the sidebar!