What Is ServiceNow Change Management?
ServiceNow Change Management is an IT Service Management (ITSM) solution designed to handle changes in an IT environment safely and efficiently. The primary goal is to implement necessary changes while minimizing the impact on services, enhancing business continuity, and aligning with regulatory requirements.
This tool enables organizations to control the lifecycle of all changes, allowing changes to be made while ensuring that standardized methods and procedures are used to understand the impact of each change, test it, and ensure it provides benefit while avoiding service disruption.
ServiceNow supports change management using traditional Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) processes, but also allows organizations to customize these processes, or design their own change management workflows.
Source: ServiceNow
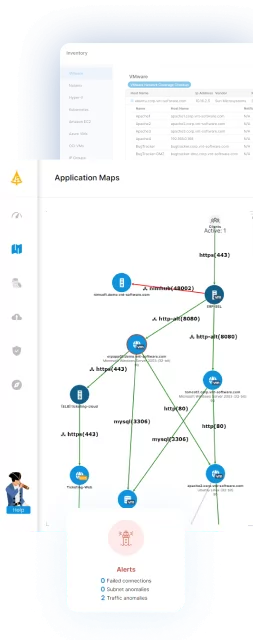
Learn more in our detailed guide to ServiceNow service mapping
Table of Contents
Toggle- What Is ServiceNow Change Management?
- Key Features of ServiceNow Change Management
- ServiceNow Change Types
- ServiceNow Supported Change Models
- ServiceNow Change Management Workflow
- ServiceNow Change Management Limitations
- Faddom: Supporting ServiceNow Change Management with Application Dependency Mapping
Key Features of ServiceNow Change Management
1. Multimodal Change
This feature introduces customizable templates that enable change managers to adapt workflows and change activities specifically tailored to varying use cases. It builds on the traditional ITIL-based out-of-the-box (OOB) change types and workflows, allowing for a seamless transition to more specialized “fit for purpose” models.
By leveraging the new flow designer tool, organizations can refine their change management processes without sacrificing their existing IT investments.
2. Change Approval Policies
ServiceNow’s change approval policies simplify and standardize the approval process for changes, ensuring that the right stakeholders are involved and decisions are made quickly. By setting up these policies, organizations can automate approvals based on predefined criteria, reducing the time and effort required for manual evaluations. For example, changes with low risk and high success scores may be automatically approved, while high-risk changes could be routed to specific individuals or the Change Advisory Board (CAB) for further review.
Change approval policies provide additional flexibility via dynamic routing. This ensures the appropriate approval chain is engaged depending on the nature, priority, or business impact of the change.
3. Change Success Score
ServiceNow’s Change Success Score automates the approval process for IT changes by assigning a numerical value that reflects a group’s historical success in implementing changes. This score significantly reduces the necessity for manual approvals, accelerates the workflow process, and helps predict the likelihood of future success.
This metric enables organizations to streamline their change management activities, ensuring faster and more effective decision-making.
4. Change Advisory Board (CAB) Workbench
The Change Advisory Board (CAB) Workbench in ServiceNow enhances the management of change advisory board meetings. It provides tools to automate the scheduling, planning, and management of these meetings through a dedicated service portal. Additionally, the workbench includes an integrated change conflict calendar, which aids in visually identifying potential conflicts between proposed changes.
5. Risk Intelligence
Risk Intelligence in ServiceNow leverages machine learning to enhance traditional change risk analysis methods. This feature offers users the choice between classification or similarity algorithms to generate data-driven risk predictions.
By integrating a machine learning-based risk prediction framework with existing risk conditions and assessments, ServiceNow automatically creates a risk profile for each proposed change. This allows organizations to better understand the potential risks associated with changes and make more informed decisions.
This is part of a series of articles about Servicenow CMDB
ServiceNow Change Types
There are three types of changes managed in ServiceNow Change Management.
Standard
A standard change is recognized as a low-risk, frequently occurring change that adheres to a specific, predefined procedure. This type of change has repeatable steps and a consistent success history.
The process for a standard change is streamlined due to its pre-authorized status, which eliminates the need for extensive approvals typically required from group levels or the Change Advisory Board (CAB).
In ServiceNow, standard changes can be cataloged in predefined templates, allowing easy access and execution while enabling the change management team to oversee and manage these pre-approved changes.
Emergency
Emergency changes are crucial for addressing urgent issues, such as resolving significant incidents or applying critical security patches. These changes are prioritized highly and expedite the usual review processes, moving directly to the Authorization state for CAB group approval.
The types of situations covered by emergency changes include critical failures where service impact is imminent or has already occurred. Due to the urgent nature of these changes, they bypass standard lifecycle stages of normal changes and may also involve unplanned Configuration Item (CI) change activities, leading to the creation and approval of unauthorized change requests in certain scenarios. This fast-tracked process ensures that emergency changes are implemented quickly to mitigate immediate risks or restore services.
Normal
A normal change in ServiceNow includes any service modifications that do not qualify as either standard or emergency changes. This category requires a more detailed approval and review process, involving two distinct levels of authorization before implementation.
Normal changes are subject to a comprehensive assessment that includes peer or technical approvals, change management oversight, and necessary CAB authorization, ensuring that each change is thoroughly evaluated for accuracy and minimal service disruption.
ServiceNow Supported Change Models
ServiceNow provides several change models that help organizations manage different types of changes based on their specific requirements. These models offer a structured approach to processing change requests. The base models fall into one of two categories:
- ITIL mode 1: A traditional, sequential approach to process Change Requests.
- ITIL mode 2: An adaptable approach that helps expedite change requests. It includes options to ensure a change isn’t a blocker to another change.
The following table summarizes the main change models:
| Change Model | Description |
| Normal | Used for ITIL mode 1 Normal changes, where a sequential process ensures successful changes. |
| Emergency | Designed for ITIL mode 1 Emergency changes, expediting urgent changes to prevent service impact. |
| Standard | Supports ITIL mode 1 Standard changes with pre-approved workflows for low-risk, routine tasks. |
| Change Registration | Facilitates external system change requests without requiring approvals. |
| Cloud Infrastructure | Manages changes related to commissioning and decommissioning cloud services. |
| Site Reliability Ops | Tailored for site reliability operations to ensure seamless workflows. |
| Unauthorized Change | Created from unauthorized change events to capture and manage unplanned changes. |
These change models are built on existing ITIL Out-of-the-Box (OOB) workflows, but are adaptable to fit specific business needs. Change managers can define unique state models, transitions, and conditions to ensure that every change is processed in a way that aligns with organizational goals. Models can be customized using ServiceNow’s Flow Designer.
ServiceNow Change Management Workflow
Here’s an overview of how ServiceNow Change Management helps teams manage changes. While the exact workflow will depend on the change model selected, most workflows will contain the steps below.
Creating a Change Request
Initiating a change starts with creating a detailed change request in ServiceNow. This entails filling a form that outlines the need for the change, the desired outcomes, and any potential impacts, ensuring all relevant information is considered right from the beginning.
A well-documented request helps in clear communication and sets the foundation for the following steps in the process.
Reviewing the Change
Once a change request is submitted, it undergoes an initial review to assess its validity and completeness. This step ensures all necessary information is included and aligns with business objectives and IT policies.
The review process may involve multiple stakeholders, who evaluate the proposed changes’ rationale, potential impacts, and benefits, ensuring that it is worth pursuing further evaluation and approvals.
Evaluating the Change
Change evaluation is where the full impact of the proposed change is analyzed. This involves looking at the technical aspects, potential disruptions, resource requirements, and alignment with strategic goals.
ServiceNow provides automated success scores and risk evaluation based on machine learning algorithms, to make change evaluation easier and enable automatic evaluation of simpler changes.
Approving the Change
For a change to proceed, it must receive approvals from relevant authorities within the organization. This usually includes IT managers, department heads, and sometimes, the Change Advisory Board.
The approval process is crucial for ensuring that the change is necessary, beneficial, and does not introduce undue risk to the environment. It acts as a final checkpoint before moving on to implementation. As mentioned, in ServiceNow it is possible to automatically approve certain types of changes based on automated evaluations or predefined change templates.
Implementing and Validating the Change
Implementation of the change is carefully planned and executed according to the predefined steps. Post-implementation, validation is carried out to ensure that the change has been completed as intended and is performing as expected.
This final stage confirms the success of the change, with lessons learned documented for future reference, thus closing the loop in the change management process.
ServiceNow Change Management Limitations
While ServiceNow Change Management is a powerful tool, it also has some limitations. The following limitations were reported by users on the G2 platform.
Complex Implementation and Customization
Implementing, configuring, and customizing ServiceNow can present significant challenges, especially for organizations with limited IT resources or experience. The complexity of tailoring the platform to meet specific business needs often requires knowledgeable administrators and might necessitate additional training for both administrators and end users to ensure they can utilize the system effectively.
Cost and Support of Plugins
The cost of plugins in ServiceNow is often considered high, which can be a barrier for some organizations looking to extend the platform’s functionality. A significant drawback is that customized widgets or applications may not receive future updates, which can affect the longevity and scalability of these solutions.
Limitations of Reporting Tools
ServiceNow’s reporting tools are not as robust as those offered by some other IT service management solutions. This limitation can impact organizations that rely heavily on advanced reporting and analytics to drive decision-making and improve IT service processes. While customization of reports is possible, it can add another layer of complexity and maintenance challenges over time.
Faddom: Supporting ServiceNow Change Management with Application Dependency Mapping
Faddom is a lightweight alternative to ServiceNow. It is agentless, doesn’t require credentials, and is cost-effective, starting at $10K/year. Faddom can map your entire environment in real-time, updating 24/7. Only one person can map an entire organization in under an hour.
Learn more about Faddom for application mapping or start a free trial to the right