What Is Cloud to Cloud Migration?
Cloud to cloud migration involves transferring data, applications, and workloads from one cloud service provider to another. This process enables businesses to take advantage of the best features, pricing models, and services offered by different providers.
The migration typically includes moving virtual machines, databases, storage systems, and applications, often with the goal of enhancing performance, improving scalability, and reducing costs. Cloud to cloud migration can be complex, requiring careful planning to minimize downtime and ensure data integrity throughout the transition.
This is part of a series about Data Center Migration
Table of Contents
ToggleBenefits of Migrating Between Cloud Providers
Migrating between cloud providers offers several substantial benefits, including:
- Cost optimization: Different cloud providers offer varying pricing models. By migrating, businesses can take advantage of more favorable rates or billing structures, potentially saving significant amounts on cloud expenditures.
- Enhanced performance: Some cloud providers offer specialized hardware or optimized networking that can improve application performance. By moving to a provider with better infrastructure, businesses can achieve faster response times and more reliable service.
- Access to advanced features: Providers frequently update their services, and by migrating, businesses can gain access to cutting-edge tools and features that may not be available from their current provider. This can include advanced data analytics, AI/ML capabilities, and improved security measures.
- Geographic reach and compliance: Some providers have data centers in specific regions that can help meet regulatory requirements or improve service delivery to customers in those areas. Migrating can ensure compliance with local data laws and enhance user experience through reduced latency.
- Increased flexibility and innovation: Migrating to a more suitable cloud environment can provide a business with greater flexibility to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions. This agility can be a competitive advantage in rapidly evolving industries.
Cloud to Cloud Migration Challenges
While cloud to cloud migration can be very beneficial, it often presents serious challenges for organizations.
Data Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security and compliance during cloud to cloud migration is paramount. Sensitive data must be protected from potential breaches during the transfer process. This involves implementing robust encryption methods for data in transit and at rest, using secure transfer protocols, and ensuring that the new provider adheres to the same or higher security standards as the previous one.
Additionally, businesses must ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2, which may involve thorough audits and documentation of data handling practices throughout the migration.
Downtime and Performance Impacts
One of the significant challenges in cloud to cloud migration is managing downtime and performance impacts. The migration process can lead to temporary unavailability of applications, causing disruptions to business operations and potentially affecting customer satisfaction.
To mitigate these issues, migrations should be carefully planned and executed during off-peak hours. Strategies such as phased migrations, where parts of the system are migrated in stages, or running systems in parallel until the new environment is fully operational, can help minimize downtime and performance issues.
Compatibility Issues
Compatibility issues are common during cloud to cloud migrations due to differences in APIs, data formats, and underlying technologies used by different providers. These discrepancies can lead to complications when transferring applications and data.
A thorough assessment of the destination environment’s compatibility with existing applications and data structures is necessary. Solutions may include modifying applications to fit the new environment, utilizing middleware to bridge compatibility gaps, or converting data formats to ensure seamless integration.
Vendor Lock-in and Flexibility
Vendor lock-in is a significant concern when businesses become overly dependent on a single cloud provider, making it difficult to switch providers or leverage competitive offerings. This lack of flexibility can hinder a company’s ability to optimize costs or adopt new technologies.
To avoid vendor lock-in, businesses should design their cloud architecture to be as portable as possible, using open standards and avoiding proprietary services that are not easily transferable. This approach facilitates easier migration and adaptation to changing business needs.

Lanir specializes in founding new tech companies for Enterprise Software: Assemble and nurture a great team, Early stage funding to growth late stage, One design partner to hundreds of enterprise customers, MVP to Enterprise grade product, Low level kernel engineering to AI/ML and BigData, One advisory board to a long list of shareholders and board members of the worlds largest VCs
Tips from the Expert
In my experience, here are tips that can help you succeed in cloud-to-cloud migration:
-
Design for multi-cloud portability
Use open-source tools, containerization (e.g., Kubernetes), and APIs to create architectures that are not tied to proprietary services, reducing future migration challenges.
-
Validate inter-cloud networking early
Ensure connectivity between clouds is optimized for low latency and high bandwidth. Pre-test network setups to avoid unexpected performance bottlenecks during migration.
-
Create a rollback plan
Always have a rollback strategy to revert to the original cloud environment if issues arise during migration. This mitigates risks and avoids prolonged downtime.
-
Leverage snapshot-based migration
Use cloud-native snapshot tools or third-party solutions to create point-in-time copies of workloads. These can simplify data transfer and ensure integrity during migration.
-
Monitor cost implications post-migration
Once the migration is complete, monitor costs in the new environment to ensure projected savings align with actual expenses. Adjust configurations as needed to avoid overspending.
Pro Tips for Successful Cloud to Cloud Migration
1. Comprehensive Planning
A successful cloud to cloud migration begins with a thorough evaluation of the current infrastructure, including an inventory of all applications, data, and workloads that need to be migrated. Understanding dependencies between different systems and applications is crucial, as this information helps in identifying the sequence in which components should be migrated to minimize disruptions.
The planning phase should also involve setting clear objectives for the migration, such as cost reduction, performance improvement, or access to new features. These objectives will guide the entire migration process. Detailed timelines and milestones should be established to track progress and ensure that the migration stays on schedule. It’s important to assign specific roles and responsibilities to team members, ensuring that everyone knows their tasks and deadlines. Risk management is another critical aspect of planning.
2. Analyze Source and Target Environments with Application Dependency Mapping
A thorough analysis of both the source and target environments is critical for a successful cloud to cloud migration. Application dependency mapping helps identify how different applications and services interact within the current infrastructure. This understanding is essential to ensure that these relationships are preserved or appropriately reconfigured in the new environment.
Application dependency mapping involves documenting all applications, services, and their dependencies, including databases, middleware, and network configurations. Application dependency mapping (ADM) software can automate this process, providing a visual representation of dependencies. This step helps in planning the migration sequence, preventing disruptions caused by broken dependencies, and ensuring that all necessary components are migrated together.
By analyzing both environments and understanding dependencies, organizations can plan the migration in a way that minimizes risks, optimizes performance, and ensures compatibility in the target cloud.
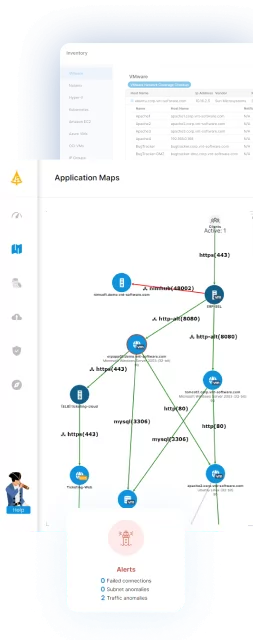
Analyzing source and target environments with Faddom
Faddom’s application dependency mapping provides critical information you’ll need before migrating workloads between clouds, automatically discovering all applications and their dependencies in both source and target environments.
Faddom is agentless and doesn’t require credentials to scan your environment. It is cheap, starting at $10K/year, and maps the entire environment in real-time, automatically updating maps 24/7. One person can map a large-scale cloud environment in an hour.
Learn more about Faddom for data center migration or try it yourself with a free trial!
3. Choose the Right Cloud Migration Tools
Cloud migration is typically performed with the help of automated tools. These tools can automate many aspects of the migration, reducing the potential for human error and speeding up the process. Key features to look for in migration tools include automated data transfer, real-time synchronization, and robust monitoring capabilities.
Most cloud providers offer free migration tools that can help organizations move workloads into their cloud platform. For example, AWS Migration Hub, Google Cloud Migrate, and Azure each offer a suite of tools designed to facilitate various aspects of migration. AWS Migration Hub provides a centralized location to track the progress of application migrations across multiple AWS and partner solutions. Google Cloud Migrate offers specialized tools for migrating virtual machines, databases, and applications with minimal disruption. Azure Migrate includes a comprehensive set of tools for discovery, assessment, and migration.
There are also third-party migration tools available which provide more advanced migration features and are able to support multiple clouds and on-premises environments. with a unified process and workflow.
4. Risk Assessment and Management
Conducting a thorough risk assessment is essential to identify potential issues that could arise during the migration process. This involves evaluating the security vulnerabilities associated with transferring data between cloud providers.
Ensuring that data remains encrypted during transit and at rest is vital to maintaining security. Assessing compliance risks is also crucial, especially for businesses that must adhere to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2. This might involve conducting audits and documenting data handling practices to ensure regulatory compliance.
Operational risks, such as potential downtime and its impact on business continuity, must be assessed and mitigated. Developing a risk management plan that includes strategies for addressing identified risks is crucial. This plan might involve additional security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, backup plans to restore data in case of a failure, and disaster recovery capabilities to ensure quick recovery from any unexpected issues.
5. Pilot Testing
Pilot testing is a critical step in the migration process that involves testing the migration with a small subset of data and applications before proceeding with the full-scale migration. This approach allows for the identification and resolution of potential issues in a controlled environment, reducing the risk of major disruptions during the actual migration.
During pilot testing, focus on migrating a representative sample of data and applications that mimic the complexity and interdependencies of the entire system. This will help uncover compatibility issues, performance impacts, and other challenges that may not have been apparent during the planning phase. By resolving these issues during the pilot phase, you can ensure a smoother and more predictable migration process.
Additionally, pilot testing provides an opportunity to validate the effectiveness of the chosen migration tools and strategies. It allows for adjustments to be made to the migration plan based on real-world feedback, ensuring that the final migration process is as efficient and error-free as possible.
6. Post-Migration Testing and Validation
After the migration is complete, thorough testing and validation are essential to ensure that all systems and applications are functioning correctly in the new cloud environment. This process should include several key activities:
-
- Data integrity verification: Ensure that all data has been accurately transferred and that no data has been lost or corrupted during the migration. This involves comparing the data in the new environment with the original data to verify its completeness and accuracy.
-
- Performance benchmarks: Conduct performance testing to ensure that the applications and systems are operating at expected levels. This includes checking response times, throughput, and resource utilization to identify any performance bottlenecks or issues.
-
- User access controls: Verify that user access controls and permissions have been correctly migrated and that users can access the applications and data they need without any issues. This is particularly important for maintaining security and compliance.
-
- Functional testing: Perform comprehensive functional testing to ensure that all applications are working as intended in the new environment. This includes testing application workflows, integrations, and any custom configurations to ensure they are functioning correctly.
-
- Monitoring and optimization: Set up monitoring tools to continuously track the performance and health of the migrated applications and infrastructure. This allows for the early detection and resolution of any issues that may arise post-migration. Regularly review and optimize the environment to ensure it continues to meet business requirements and performance expectations.
Related content: Read our guide to cloud migration strategy
Conclusion
Cloud to cloud migration offers businesses significant benefits, including cost optimization, enhanced performance, and access to advanced features. However, it also presents challenges such as ensuring data security, managing downtime, and addressing compatibility issues. By following best practices, including comprehensive planning, dependency mapping, selecting the right tools, risk assessment, pilot testing, and post-migration validation, organizations can navigate the complexities of cloud to cloud migration effectively.
Learn more about Faddom for data center migration or try it yourself with a free trial!